Inhibition of the Naja naja venom toxicity by polymeric nanoparticles loaded with Leucas aspera methanolic extract
- PMID: 38783952
- PMCID: PMC11112068
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1385213
Inhibition of the Naja naja venom toxicity by polymeric nanoparticles loaded with Leucas aspera methanolic extract
Abstract
Background: Snakebite is a neglected tropical disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Developing effective treatments can make a significant contribution to global health efforts and public health initiatives. To reduce mortality due to snakebite, there is an immediate need to explore novel and effective treatment methodologies. In that context, nanoparticle-based drug delivery is gaining a lot of attention. Hydrophilic nanoparticles are suitable for the delivery of therapeutic peptides, proteins, and antigens.
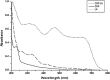
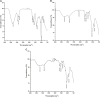
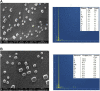
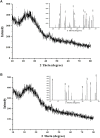
Methods: The present investigation is aimed at evaluating the anti-ophidian potential of the methanolic extract of the ethno-medicinal herb Leucas aspera (Willd.) loaded within chitosan nanoparticles (CNP-LA), against the Indian cobra (Naja naja) venom enzymes. For this purpose, nanoparticles were prepared using the ionic gelation method to enhance the efficacy of the extract. The physicochemical and structural features of nanoparticles were investigated using dynamic light scattering (DLS), Fourier-transform Infrared (FTIR), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques.
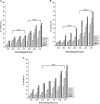
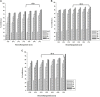
Results: It was found that CNP-LA has an average size of 260 nm with a polydispersity index of 0.132 (PDI) and zeta potential of 34.7 mV, with an encapsulation efficiency of 92.46%. The in vitro release study was performed at pH 5.0 and 7.4. Furthermore, in vitro studies indicated that CNP-LA inhibited the phospholipase A2, hemolytic, and caseinolytic activities of Naja naja venom with the percentage inhibition of 92.5%, 83.9%, and 94.5%, respectively.
Conclusion: This is the first report on the application of herbal methanolic extract loaded within chitosan nanoparticles for neutralizing snake venom enzymes with increased efficiency.
Keywords: Leucas aspera (Willd.); Naja naja; chitosan; controlled release; nanoparticle.
Copyright © 2024 Singh and Jayaraman.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Naja naja venom enzymes by the methanolic extract of Leucas aspera and its chemical profile by GC-MS.Toxicol Rep. 2014 Aug 29;1:667-673. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.08.012. eCollection 2014. Toxicol Rep. 2014. PMID: 28962280 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles containing Naja naja oxiana snake venom.Nanomedicine. 2010 Feb;6(1):137-43. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Jul 16. Nanomedicine. 2010. PMID: 19616121
-
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Indian male fern (Dryopteris Cochleata), operational parameters, characterization and bioactivity on Naja naja venom neutralization.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2020 Oct 15;9(5):706-713. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaa070. eCollection 2020 Sep. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2020. PMID: 33178431 Free PMC article.
-
Antivenom activity of triterpenoid (C34H68O2) from Leucas aspera Linn. against Naja naja naja venom induced toxicity: antioxidant and histological study in mice.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014 Apr;33(4):336-59. doi: 10.1177/0960327113494901. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 23857030
-
Protective activity of medicinal plants and their isolated compounds against the toxic effects from the venom of Naja (cobra) species.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Nov 18;157:222-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.09.039. Epub 2014 Oct 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25291011 Review.
References
-
- Achyuthan K. E., Ramachandran L. K. (1981). Cardiotoxin of the Indian cobra (Naja naja) is a pyrophosphatase. J. Biosci. 3, 149–155. 10.1007/BF02702658 - DOI
-
- Agarwal M., Agarwal M. K., Shrivastav N., Pandey S., Das R., Gaur P. (2018). Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles and their in-vitro characterization. Int. J. Life-Sciences Sci. Res. 4, 1713–1720. 10.21276/ijlssr.2018.4.2.17 - DOI
-
- Alqahtani M. S., Al-Yousef H. M., Alqahtani A. S., Tabish Rehman M., AlAjmi M. F., Almarfidi O., et al. (2021). Preparation, characterization, and in vitro-in silico biological activities of Jatropha pelargoniifolia extract loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 606, 120867. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120867 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anandalakshmi K., Venugobal J., Ramasamy V. (2016). Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 399–408. 10.1007/s13204-015-0449-z - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

