Investigation of the molecular mechanism of Smilax glabra Roxb. in treating hypertension based on proteomics and bioinformatics
- PMID: 38783958
- PMCID: PMC11112092
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1360829
Investigation of the molecular mechanism of Smilax glabra Roxb. in treating hypertension based on proteomics and bioinformatics
Abstract
Background: Smilax glabra Roxb. (named tufuling in Chinese, SGR) has both medicinal and edible value. SGR has obvious pharmacological activity, especially in anti-inflammation and treating immune system diseases. This study investigated differential protein expression and its relationship with immune infiltration in hypertension treated with SGR using proteomics and bioinformatics.
Methods: N-Nitro L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) was used to replicate the hypertension model, with SGR administered by gavage for 4 weeks, and the systolic and diastolic blood pressure in each group of rats was measured using the tail-cuff method every 7 days. Furthermore, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to determine the serum total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) expressions in each group, followed by the detection of protein expression in rat liver samples using the tandem mass tag (TMT) technique. Additionally, hub targets were output using Cytoscape 3.9.1 software, and ALDH2 expression in the liver and serum in each group of rats was detected by ELISA. Moreover, R4.3.0 software was used to evaluate the relationship between acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) and immune cells, and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) was performed to identify the components of SGR. Furthermore, the association between components of SGR and ALDH2 was analyzed with molecular docking and LigPlot1.4.5 software.
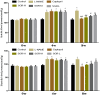
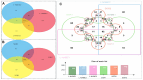
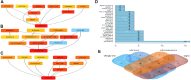
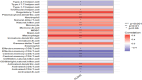
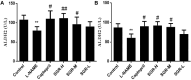
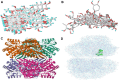
Results: Compared with the model group (L-NAME), SGR at high and medium doses reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure while reducing TC, TG, and LDL-C levels and increasing HDL-C levels in hypertensive rats (p < 0.05). Moreover, 92 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were identified using TMT. These DEPs participated in peroxisome functioning, fatty acid degradation, and other signaling pathways, with ALDH2 being the core target and correlated with various immune cells. In addition, 18 components were determined in SGR, with 8 compounds binding to ALDH2. Molecular docking was performed to confirm that SGR played a role in hypertension based on the combined action of multiple components.
Conclusion: In conclusion, SGR has an antihypertensive effect on L-NAME-induced hypertension, with ALDH2 as its hub target. SGR may regulate neutrophil, regulatory T cell, and other cells' infiltration by targeting ALDH2, thereby contributing to the treatment of hypertension.
Keywords: ALDH2; Smilax glabra Roxb.; high blood pressure; immune cell infiltration; proteomics.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Qian, Yang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Comprehensive characterisation of the active ingredients of Smilax glabra Roxb based on chemical fingerprinting, metabolic fingerprinting and pharmacodynamic fingerprinting.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 23;16:1519054. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1519054. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40337523 Free PMC article.
-
Lei-gong-gen formula granule attenuates hyperlipidemia in rats via cGMP-PKG signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:112989. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112989. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32526339
-
Discovery of the active compounds of Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma by utilizing the relationship between the individual differences in blood drug concentration and the pharmacological effect in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Aug 10;258:112886. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112886. Epub 2020 Apr 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32325179
-
Ethnomedicine, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Smilax glabra: An Important Traditional Chinese Medicine.Am J Chin Med. 2018;46(2):261-297. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X18500143. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Am J Chin Med. 2018. PMID: 29433390 Review.
-
Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on metabolic syndrome.J Ginseng Res. 2021 May;45(3):380-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34025131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Profiling and Wound Healing Activity of Gigantochloa apus Liquid Smoke in Mus Musculus.J Exp Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 4;16:339-350. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S479862. eCollection 2024. J Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39381029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abaidullah M., La S., Liu M., Liu B., Cui Y., Wang Z., et al. (2023). Polysaccharide from Smilax glabra Roxb mitigates intestinal mucosal damage by therapeutically restoring the interactions between gut microbiota and innate immune functions. Nutrients 15, 4102. 10.3390/nu15194102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

