Prospective Randomized Trial of Na/K Citrate for the Prevention of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in High-risk Patients
- PMID: 38783979
- PMCID: PMC11114188
- DOI: 10.47176/mjiri.38.27
Prospective Randomized Trial of Na/K Citrate for the Prevention of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in High-risk Patients
Abstract
Background: Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) or contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) refers to an acute kidney injury (AKI) occurring after exposure to contrast media, commonly used in diagnostic procedures or therapeutic angiographic interventions. Recently, Na/K citrate, used for urine alkalinization, has been assessed for preventing CIN. This experiment evaluated Na/K citrate's efficacy in preventing CIN in high-risk patients undergoing cardiac catheterization.
Methods: A prospective randomized clinical trial involved 400 patients with moderate- to high-risk factors for CIN undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). They were randomly assigned to either the control or Na/K citrate groups. The Na/K citrate group (n = 200) received a 5 g Na/K citrate solution diluted in 200 mL water 2 hours before and 4 hours after the first administration, along with intravenous hydration for 2 hours before and 6 hours after the procedure. In contrast, the control group (n = 200) received only intravenous hydration. Serum creatinine (SCr) levels were measured before contrast exposure and 48 hours afterward. CIN was defined as a 25% increase in serum creatinine (SCr) or > 0.5 mg/dL 48 hours after contrast administration. The significance level was set at P ˂ 0.05.
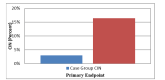
Results: CIN was observed in 33 patients (16.5%) in the control group and 6 patients (3%) in the Na/K citrate group. The incidence of CIN was found to have a significant difference between the 2 groups 48 hours after receiving the radiocontrast agent (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our results show that Na/K citrate is helpful and substantially reduces the incidence of CIN.
Keywords: Citrate; Contrast media; Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.
© 2024 Iran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
-
- Calabrò P, Bianchi R, Crisci M, Caprile M, Bigazzi MC, Palmieri R. et al. Use and efficacy of saline hydration and N-acetyl cysteine to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy in low-risk populations undergoing coronary artery angiography. J Emerg Med. 2011;6(6):503. doi: 10.1007/s11739-011-0513-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Brabec BA, Edmonds PJ, O'Corragain OA, Erickson SB. Oral hydration for prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in elective radiological procedures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. N Am J Med Sci. 2014;6(12):618. doi: 10.4103/1947-2714.147977. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous