The LysR family transcriptional regulator ORF-L16 regulates spinosad biosynthesis in Saccharopolyspora spinosa
- PMID: 38784197
- PMCID: PMC11108826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.05.001
The LysR family transcriptional regulator ORF-L16 regulates spinosad biosynthesis in Saccharopolyspora spinosa
Abstract
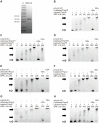
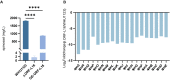
Spinosad, a potent broad-spectrum bioinsecticide produced by Saccharopolyspora spinosa, has significant market potential. Despite its effectiveness, the regulatory mechanisms of spinosad biosynthesis remain unclear. Our investigation identified the crucial role of the LysR family transcriptional regulator ORF-L16, located upstream of spinosad biosynthetic genes, in spinosad biosynthesis. Through reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and 5'-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5'-Race), we unveiled that the spinosad biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) contains six transcription units and seven promoters. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) demonstrated that ORF-L16 bound to seven promoters within the spinosad BGC, indicating its involvement in regulating spinosad biosynthesis. Notably, deletion of ORF-L16 led to a drastic reduction in spinosad production from 1818.73 mg/L to 1.69 mg/L, accompanied by decreased transcription levels of spinosad biosynthetic genes, confirming its positive regulatory function. Additionally, isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) and EMSA confirmed that spinosyn A, the main product of the spinosad BGC, served as an effector of ORF-L16. Specifically, it decreased the binding affinity between ORF-L16 and spinosad BGC promoters, thus exerting negative feedback regulation on spinosad biosynthesis. This research enhances our comprehension of spinosad biosynthesis regulation and lays the groundwork for future investigations on transcriptional regulators in S. spinosa.
Keywords: LysR family transcriptional regulator; Regulation; Saccharopolyspora spinosa; Spinosad; Spinosyn A.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors applied a patent based on this research. Zixin Deng and Tiangang Liu are Founding Editor and Editorial Board Member for Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, respectively. And they were not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enhancement of spinosad production in Saccharopolyspora spinosa by overexpression of the complete 74-kb spinosyn gene cluster.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 May 8;24(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02724-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40340747 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and analysis of the spinosad biosynthetic gene cluster of Saccharopolyspora spinosa.Chem Biol. 2001 May;8(5):487-99. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(01)00029-1. Chem Biol. 2001. PMID: 11358695
-
Exploration of Streptomyces fradiae J1-021 as a Potential Host for the Heterologous Production of Spinosad.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Apr 10. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c08884. Online ahead of print. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38597928
-
Strategies for Enhancing the Yield of the Potent Insecticide Spinosad in Actinomycetes.Biotechnol J. 2019 Jan;14(1):e1700769. doi: 10.1002/biot.201700769. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 29897659 Review.
-
[Advances in the biosynthesis of spinosad - A review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2016 Mar 4;56(3):397-405. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27382783 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
CRISPRi-mediated multigene downregulating redirects the metabolic flux to spinosad biosynthesis in Saccharopolyspora spinosa.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 20;10(2):583-592. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2025.02.010. eCollection 2025 Jun. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40092162 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of spinosad production in Saccharopolyspora spinosa by overexpression of the complete 74-kb spinosyn gene cluster.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 May 8;24(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02724-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40340747 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced triacylglycerol metabolism contributes to the efficient biosynthesis of spinosad in Saccharopolyspora spinosa.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 25;9(4):809-819. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.06.007. eCollection 2024 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39072147 Free PMC article.
-
iCASRED, a scarless DNA editing tool in E. coli for high-efficiency engineering of natural product biosynthetic gene clusters.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 20;10(3):751-763. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2025.03.008. eCollection 2025 Sep. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40248484 Free PMC article.
-
The PurR family transcriptional regulator promotes butenyl-spinosyn production in Saccharopolyspora pogona.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 21;109(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13390-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39836216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang L., Demain A. 2005. Natural products: drug discovery and therapeutic medicine.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

