Exploration of the Shared Gene Signatures and Molecular Mechanisms Between Ischemic Stroke and Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 38784404
- PMCID: PMC11114141
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S454336
Exploration of the Shared Gene Signatures and Molecular Mechanisms Between Ischemic Stroke and Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Purpose: Atherosclerosis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease and the predominant cause of ischemic stroke (IS). AS is a potential pathogenetic factor in IS. However, the processes by which they interact remain unknown. The purpose of this paper was to investigate the shared gene signatures and putative molecular processes in AS and IS.
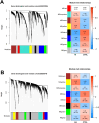
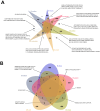
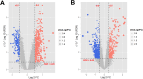
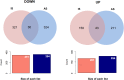
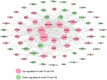
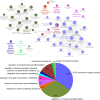
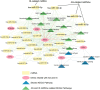
Methods: Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) data for AS and IS microarrays were retrieved. The co-expression modules associated with AS and IS were identified using the Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA). We constructed an interaction network of shared differentially expressed genes in AS and IS and conducted an enrichment analysis using ClueGO software. We validated the results in a separate cohort through differential gene analysis. Additionally, we retrieved AS and IS-related miRNAs from the Human microRNA Disease Database (HMDD) and predicted their target genes using miRWalk. We then built a network of miRNAs-mRNAs-KEGG pathways using the shared genes.
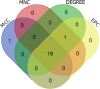
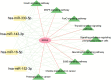
Results: Through WGCNA, we identified five modules and six modules as significant in AS and IS, respectively. A ClueGO enrichment analysis of common genes showed that highly active CCR1 chemokine receptor binding is critical to AS and IS pathogenesis. The differential analysis expression results in another cohort closely matched these findings. The miRNA-mRNA network suggested that hsa-miR-330-5p, hsa-miR-143-3p, hsa-miR-16-5p, hsa-miR-152-3p might regulate the shared gene KRAS, which could be a key player in AS and IS.
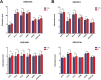
Conclusion: We integrated ischemic stroke and carotid atherosclerosis public database data and found that ATF3, CCL3, CCL4, JUNB, KRAS, and ZC3H12A may affect both, making them novel biomarkers or therapeutic target genes. Clinical samples and expression trends supported our analyses of pivotal genes.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; biomarker; co-expression; ischemic stroke; risk factors.
© 2024 Ban et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Hägg DA, Jernås M, Wiklund O, et al. Expression Profiling of Macrophages from Subjects with Atherosclerosis to Identify Novel Susceptibility Genes. IntJ Mol Med. 2008;21(6):697–704. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

