Construction of core-shell magnetic metal-organic framework composites Fe3O4@MIL-101(Fe, Co) for degradation of RhB by efficiently activating PMS
- PMID: 38784411
- PMCID: PMC11112680
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra08768a
Construction of core-shell magnetic metal-organic framework composites Fe3O4@MIL-101(Fe, Co) for degradation of RhB by efficiently activating PMS
Abstract
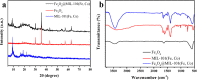
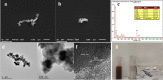
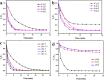
Low catalytic efficiency and catalyst recovery are the key factors limiting the practical application of advanced oxidation processes. In this work, a core-shell magnetic nanostructure Fe3O4@MIL-101(Fe, Co) was prepared via a simple solvothermal method. The core-shell structure and magnetic recovery performance were characterized by various technologies. The results of dye degradation experiments proved that within 10 minutes, the Fe3O4@MIL-101(Fe, Co)/PMS system can degrade more than 95% of 10 mg per L Rhodamine (RhB) at an initial pH of 7, which possesses higher catalytic activity than the Fe3O4/PMS system and the MIL-101(Fe, Co)/PMS system. The effects of initial solution pH and coexisting anions in water on the degradation of RhB were further discussed. The results showed that Fe3O4@MIL-101(Fe, Co) displayed excellent degradation efficiency in a wide pH range of 3-11 and capability of resisting coexisting anions. It is worth mentioning that after five cycles, the RhB removal rate can still be maintained at over 90% after 10 minutes of reaction. Free radical quenching experiments were further studied, confirming that ˙OH and SO4-˙ were involved in the degradation of RhB, while the dominating active free radical was SO4-˙. The possible reaction mechanism of the RhB degradation process was also inferred.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Degradation of Orange G Using PMS Triggered by NH2-MIL-101(Fe): An Amino-Functionalized Metal-Organic Framework.Molecules. 2024 Mar 27;29(7):1488. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071488. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611767 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient degradation of Rhodamine B by magnetically recoverable Fe3O4-modified ternary CoFeCu-layered double hydroxides via activating peroxymonosulfate.J Environ Sci (China). 2021 Oct;108:188-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2021.02.020. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Environ Sci (China). 2021. PMID: 34465432
-
Degradation of organic dyes by peroxymonosulfate activated with water-stable iron-based metal organic frameworks.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021 May;589:298-307. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.12.123. Epub 2021 Jan 5. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021. PMID: 33472149
-
Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co-Mg-Fe layered doubled hydroxide for efficient degradation of Rhodamine B.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Mar;30(13):37634-37645. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24983-6. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36574127
-
Enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation by hierarchical porous Fe3O4/Co3S4 nanosheets for efficient elimination of rhodamine B: Mechanisms, degradation pathways and toxicological analysis.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Mar 15;610:751-765. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.118. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 34857379
Cited by
-
Efficient Tetracycline Hydrochloride Degradation by Urchin-Like Structured MoS2@CoFe2O4 Derived from Steel Pickling Sludge via Peroxymonosulfate Activation.Molecules. 2025 Jul 30;30(15):3194. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153194. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varghese A. G. Paul S. A. Latha M. S. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019;17:867–877.
-
- Sriram G. Bendre A. Mariappan E. Altalhi T. Kigga M. Ching Y. C. Jung H.-Y. Bhaduri B. Kurkuri M. Sustainable Mater. Technol. 2022;31:e00378.
-
- Jorfi S. Pourfadakari S. Kakavandi B. Chem. Eng. J. 2018;343:95–107.
-
- Ma X. Zhao S. Tian Z. Duan G. Pan H. Yue Y. Li S. Jian S. Yang W. Liu K. He S. Jiang S. Chem. Eng. J. 2022;446:136851.
-
- Lin Q. Zeng G. Yan G. Luo J. Cheng X. Zhao Z. Li H. Chem. Eng. J. 2022;427:131668.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

