Natural language acquisition and gestalt language processing: A critical analysis of their application to autism and speech language therapy
- PMID: 38784430
- PMCID: PMC11113044
- DOI: 10.1177/23969415241249944
Natural language acquisition and gestalt language processing: A critical analysis of their application to autism and speech language therapy
Abstract
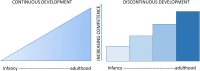
Background and aim: Recently, there has been a lot of interest surrounding the term gestalt language processor (GLP) which is associated with Natural Language Acquisition (NLA): a protocol intended to support the language development of autistic people. In NLA, delayed echolalia is presumed raw source material that GLPs use to acquire language in a stage-like progression from delayed echolalia to spontaneous speech. The aim of this article is to evaluate NLA in light of relevant literatures to allow scrutiny of NLA claims.
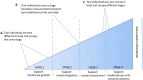
Main contributions: First, we review the notion of gestalt language and situate it in the broader literature on language styles to update understanding of its significance. We then review the links from gestalt language processing to autism and identify definitional and conceptual problems and clarify the construct 'episodic memory'. We discuss the 'raw material view of delayed echolalia' and identify theoretical and empirical shortcomings. Finally, we review Blanc's language stages and their accompanying assessment and language support recommendations and challenge their validity.
Conclusions & implications: The term 'gestalt language processor' is definitionally and conceptually troubled, the assertion that autistic people are GLPs is misleading and unhelpful, and evidence is lacking that GLP represents a legitimate clinical entity. The theoretical basis of NLA lacks empirical support. NLA stages are implausible and their accompanying assessment and support recommendations lack justification. We recommend the use of alternate, individualized, theoretically-sound, evidence-based, neurodiversity-affirming supports that are sensitive and responsive to the heterogeneity that defines autism.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorders; gestalt language; language impairment /disorder; speech and language therapy.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Abbot-Smith K. (2020). Language disorders and autism: Implications for usage-based theories of language development. In Current perspectives on child language acquisition: How children use their environment to learn (pp. 287–321). John Benjamins Publishing.
-
- Abbot-Smith K., Tomasello M. (2006). Exemplar-learning and schematization in a usage-based account of syntactic acquisition. The Linguistic Review, 23(3), 275–290. 10.1515/TLR.2006.011 - DOI
-
- Altenberg B. (1998). On the phraseology of spoken English: The evidence of recurrent word combinations. In A. P. Crowie (Ed.), Phraseology: Theory, analysis, and applications (pp. 101–122). Oxford University Press.
-
- AndNextComesL. (2024). Signs that your child is a gestalt language processor. https://www.andnextcomesl.com/2022/02/signs-of-gestalt-language-processi...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
