Integrative analysis of plasma and substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease: unraveling biomarkers and insights from the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network
- PMID: 38784444
- PMCID: PMC11112011
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1388655
Integrative analysis of plasma and substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease: unraveling biomarkers and insights from the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network
Abstract
Introduction: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a rapidly growing neurological disorder characterized by diverse movement symptoms. However, the underlying causes have not been clearly identified, and accurate diagnosis is challenging. This study aimed to identify potential biomarkers suitable for PD diagnosis and present an integrative perspective on the disease.
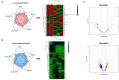
Methods: We screened the GSE7621, GSE8397-GPL96, GSE8397-GPL97, GSE20163, and GSE20164 datasets in the NCBI GEO database to identify differentially expressed (DE) mRNAs in the substantia nigra (SN). We also screened the GSE160299 dataset from the NCBI GEO database to identify DE lncRNAs and miRNAs in plasma. We then constructed 2 lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulatory networks based on the ceRNA hypothesis. To understand the biological function, we performed Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway and Gene Ontology analyses for each ceRNA network. The receiver operating characteristic analyses (ROC) was used to assess ceRNA results.
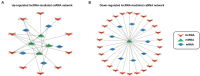
Results: We identified 7 upregulated and 29 downregulated mRNAs as common DE mRNAs in the 5 SN datasets. In the blood dataset, we identified 31 DE miRNAs (9 upregulated and 22 downregulated) and 332 DE lncRNAs (69 upregulated and 263 downregulated). Based on the determined interactions, 5 genes (P2RX7, HSPA1, SLCO4A1, RAD52, and SIRT4) appeared to be upregulated as a result of 10 lncRNAs sponging 4 miRNAs (miR-411, miR-1193, miR-301b, and miR-514a-2/3). Competing with 9 genes (ANK1, CBLN1, RGS4, SLC6A3, SYNGR3, VSNL1, DDC, KCNJ6, and SV2C) for miR-671, a total of 26 lncRNAs seemed to function as ceRNAs, influencing genes to be downregulated.
Discussion: In this study, we successfully constructed 2 novel ceRNA regulatory networks in patients with PD, including 36 lncRNAs, 5 miRNAs, and 14 mRNAs. Our results suggest that these plasma lncRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of PD by sponging miRNAs and regulating gene expression in the SN of the brain. We propose that the upregulated and downregulated lncRNA-mediated ceRNA networks represent mechanisms of neuroinflammation and dopamine neurotransmission, respectively. Our ceRNA network, which was associated with PD, suggests the potential use of DE miRNAs and lncRNAs as body fluid diagnostic biomarkers. These findings provide an integrated view of the mechanisms underlying gene regulation and interactions in PD.
Keywords: GEO database; Parkinson’s disease; bioinformatics analysis; biomarker; ceRNA network; lncRNA; meta-analysis; microRNA.
Copyright © 2024 Chun and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identifying a Comprehensive ceRNA Network to Reveal Novel Targets for the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease.Front Neurol. 2020 Aug 4;11:810. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00810. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32849243 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA Network in Alzheimer's Disease.J Integr Neurosci. 2023 Oct 17;22(6):136. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2206136. J Integr Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38176923
-
Non-coding RNA Identification in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Using Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Analysis.Orthop Surg. 2021 May;13(3):1067-1076. doi: 10.1111/os.12834. Epub 2021 Mar 21. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33749138 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of an lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network in pulpitis.PeerJ. 2019 Jun 17;7:e7135. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7135. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31304055 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs regulation in Parkinson's disease, and their potential role as diagnostic and therapeutic targets.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Oct 5;10(1):186. doi: 10.1038/s41531-024-00791-2. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 39369002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Calzaferri F., Ruiz-Ruiz C., De Diego A. M. G., De Pascual R., Mendez-Lopez I., Cano-Abad M. F., et al. . (2020). The purinergic P2X7 receptor as a potential drug target to combat neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Med. Res. Rev. 40, 2427–2465. doi: 10.1002/med.21710, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

