Assessment of Epidemiological Indicators for Evaluation of National Malaria Elimination Programme: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38784487
- PMCID: PMC11111267
- DOI: 10.4314/ejhs.v33i6.12
Assessment of Epidemiological Indicators for Evaluation of National Malaria Elimination Programme: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Background: Malaria has been one of India's most considerable health problems since 1940. The objective of our study is to determine the status of the National Malaria Elimination Programme in India by using epidemiological indicators.
Methods and materials: The annual reports of malaria for the years 2014-2021 and monthly reports for 2020 and 2021 were collected from the official web portal and were analysed for study specific assessments.
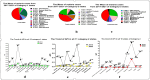
Results: The API has shown a statistically significant reduction from 2017-2021 in all states along with category-1(P=0.003) and category-2(P=0.029) states/UTs, but there was no statistically significant reduction from 2017-2021 in category-3 (P=0.166) states/UTs. The zero indigenous cases had not been achieved in category-1 states/UTs. The overall percentage reduction in number of malaria cases in 2020 at the national level compared with 2014 was 83.6%. Despite states with strong health systems such as Gujarat, Maharashtra and Karnataka, have not shown zero indigenous cases in 2020 and the malaria cases noted were very far from reaching the targets.
Conclusions: Although we observed a significant drop in malaria incidence from 2014 to 2020, demonstrating that the country is moving nearer to malaria elimination, it is crucial to implement the strategies to reduce Plasmodium falciparum% and re-establish surveillance programmes and execute national and state programmes in order to achieve the success of the National Malaria Elimination Programme. The recategorization of states/UTs are in accordance to the API, and implementation strategies were also needed.
Keywords: Annual Parasite Incidence; Malaria; National Framework for Malaria Elimination in India; National Malaria Elimination Programme; Plasmodium falciparum.
© 2023 Hima S.P, et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ready for malaria elimination: zero indigenous case reported in the People's Republic of China.Malar J. 2018 Aug 29;17(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2444-9. Malar J. 2018. PMID: 30157876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From control to elimination: a spatial-temporal analysis of malaria along the China-Myanmar border.Infect Dis Poverty. 2020 Nov 19;9(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00777-1. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020. PMID: 33213516 Free PMC article.
-
Malaria elimination in India-The way forward.J Vector Borne Dis. 2019 Jan-Mar;56(1):32-40. doi: 10.4103/0972-9062.257771. J Vector Borne Dis. 2019. PMID: 31070163 Review.
-
Malaria control in Bhutan: case study of a country embarking on elimination.Malar J. 2012 Jan 9;11:9. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-9. Malar J. 2012. PMID: 22230355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digitized smart surveillance and micromanagement using information technology for malaria elimination in Mangaluru, India: an analysis of five-year post-digitization data.Malar J. 2021 Mar 8;20(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03656-8. Malar J. 2021. PMID: 33685454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World malaria report 2022 (Internet) 2022. [December 02 2022]. www.who.int. Available from: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/reports/world-malaria....
-
- Fact sheet about malaria (Internet) 2023. Jan 27, www.who.int. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malaria#:~:text=resista....
-
- World Health Organization, author. Global Malaria Programme. Countries where malaria never existed or disappeared without specific measures. [September 19 2022]. Available from: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/elimination/countries....
-
- Dhamnetiya D, Sahu M. Malaria Control in India: Strategies, Progress and Challenges. Int J Contemp Med. 2015 Jan;3(1):14.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
