Pest categorisation of Shirahoshizo flavonotatus
- PMID: 38784846
- PMCID: PMC11112459
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8805
Pest categorisation of Shirahoshizo flavonotatus
Abstract
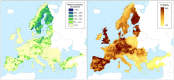
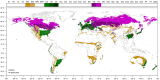
The EFSA Panel on Plant Health performed a pest categorisation of Shirahoshizo patruelis (Voss, 1937) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), following the commodity risk assessment of bonsai plants from China consisting of Pinus parviflora grafted on P. thunbergii, in which S. patruelis was identified as a pest of possible concern to the European Union (EU). This categorisation refers to S. flavonotatus, which is the pest's current valid scientific name. It is native to China and has never been recorded in the EU. It completes from 2 to 3 generations per year. Eggs are laid in cracks and crevices of trunks and branches with bark thickness of approximately 0.6-1.2 cm. The pest overwinters as an adult or as a mature larva under the bark. Plants for planting, wood with bark and wood products provide pathways for entry. Although the weevil has been reported to carry the nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, it is not considered a vector. Climatic conditions and availability of host plants in some EU countries would allow S. flavonotatus to establish and spread. Impact on Pinus spp. is anticipated. Recognising that the weevil is reported to attack both weakened and healthy trees, there is uncertainty on the magnitude of impact. Its recorded capacity to attack non-Asian Pinus species also indicates its ability to adapt and expand the range of trees it can utilise as hosts, which could include European Pinus species. Phytosanitary measures are available to reduce the likelihood of entry and spread. S. flavonotatus meets the criteria that are within the remit of EFSA to assess for this species to be regarded as a potential Union quarantine pest.
Keywords: Pinus; pest risk; plant health; plant pest; quarantine; weevil.
© 2024 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Conflict of interest statement
If you wish to access the declaration of interests of any expert contributing to an EFSA scientific assessment, please contact interestmanagement@efsa.europa.eu.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pest categorisation of Dendrolimus punctatus.EFSA J. 2024 Mar 5;22(3):e8504. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8504. eCollection 2024 Mar. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 38444826 Free PMC article.
-
Pest categorisation of Matsucoccus matsumurae.EFSA J. 2024 Jul 19;22(7):e8970. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8970. eCollection 2024 Jul. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 39036775 Free PMC article.
-
Pest categorisation of Garella musculana.EFSA J. 2024 Mar 7;22(3):e8646. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8646. eCollection 2024 Mar. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 38455155 Free PMC article.
-
Pest categorisation of Ceroplastes rubens.EFSA J. 2024 Jul 10;22(7):e8888. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8888. eCollection 2024 Jul. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 38993592 Free PMC article.
-
Pest categorisation of Pyrrhoderma noxium.EFSA J. 2024 Mar 19;22(3):e8667. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8667. eCollection 2024 Mar. EFSA J. 2024. PMID: 38505477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbulut, S. , & Stamps, W. T. (2011). Insect vectors of the pinewood nematode: A review of the biology and ecology of Monochamus species. Forest Pathology, 42, 89–99.
-
- Alonso‐Zarazaga, M. A. , Barrios, H. , Borovec, R. , Bouchard, P. , Caldara, R. , Colonnelli, E. , Gültekin, L. , Hlaváč, P. , Korotyaev, B. , Lyal, C. H. C. , Machado, A. , Meregalli, M. , Pierotti, H. , Ren, L. , Sánchez‐Ruiz, M. , Sforzi, A. , Silfverberg, H. , Skuhrovec, J. , Trýzna, M. , … Yunakov, N. N. (2017). Cooperative catalogue of Palaearctic Coleoptera Curculionoidea. Monografías electrónicas Sociedad Entomológica Aragonesa, 8, 1–729.
-
- Baker, R. H. A. (2002). Predicting the limits to the potential distribution of alien crop pests. In Hallman G. J. & Schwalbe C. P. (Eds.), Invasive arthropods in agriculture: Problems and solutions (pp. 207–241). Science Publishers Inc.
-
- Bossard, M. , Feranec, J. , & Otahel, J. (2000). CORINE land cover technical guide—Addendum 2000 . Tech. Rep. 40, European Environment Agency. https://www.eea.europa.eu/ds_resolveuid/032TFUPGVR
-
- Büttner, G. , Kosztra, B. , Maucha, G. , & Pataki, R. (2012). Implementation and achievements of CLC2006 . Tech. rep., European Environment Agency. http://www.eea.europa.eu/ds_resolveuid/GQ4JECM8TB
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
