Caenorhabditis elegans neuropeptide NLP-27 enhances neurodegeneration and paralysis in an opioid-like manner during fungal infection
- PMID: 38784855
- PMCID: PMC11112505
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109484
Caenorhabditis elegans neuropeptide NLP-27 enhances neurodegeneration and paralysis in an opioid-like manner during fungal infection
Abstract
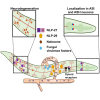
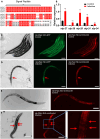
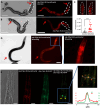
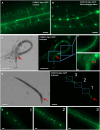
The nervous system of metazoans is involved in host-pathogen interactions to control immune activation. In Caenorhabditis elegans, this includes sleep induction, mediated by neuropeptide-like proteins (NLPs), which increases the chance of survival after wounding. Here we analyzed the role of NLP-27 in the infection of C. elegans with the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys flagrans. Early responses of C. elegans were the upregulation of nlp-27, the induction of paralysis (sleep), and neurodegeneration of the mechanosensing PVD (Posterior Ventral Process D) neurons. Deletion of nlp-27 reduced neurodegeneration during fungal attack. Induction of nlp-27 was independent of the MAP kinase PMK-1, and expression of nlp-27 in the hypodermis was sufficient to induce paralysis, although NLP-27 was also upregulated in head neurons. NLP-27 contains the pentapeptide YGGYG sequence known to bind the human μ- and κ-type opioid receptors suggesting NLP-27 or peptides thereof act on opioid receptors. The opioid receptor antagonist naloxone shortened the paralysis time like overexpression of NLP-27.
Keywords: Immunology; Molecular neuroscience; Neuroscience.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Opiates Modulate Noxious Chemical Nociception through a Complex Monoaminergic/Peptidergic Cascade.J Neurosci. 2016 May 18;36(20):5498-508. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4520-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27194330 Free PMC article.
-
The actions of Caenorhabditis elegans neuropeptide-like peptides (NLPs) on body wall muscle of Ascaris suum and pharyngeal muscle of C. elegans.Acta Biol Hung. 2008;59 Suppl:189-97. doi: 10.1556/ABiol.59.2008.Suppl.28. Acta Biol Hung. 2008. PMID: 18652392
-
Neuropeptide-like protein diversity in phylum Nematoda.Int J Parasitol. 2008 Nov;38(13):1493-503. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2008.05.006. Epub 2008 May 25. Int J Parasitol. 2008. PMID: 18602104
-
Neuropeptide gene families in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;897:239-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07895.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10676452 Review.
-
Comparison of Caenorhabditis elegans NLP peptides with arthropod neuropeptides.Trends Parasitol. 2009 Apr;25(4):171-81. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2008.12.009. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Trends Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19269897 Review.
Cited by
-
Predation by nematode-trapping fungus triggers mechanosensory-dependent quiescence in Caenorhabditis elegans.iScience. 2025 May 30;28(7):112792. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112792. eCollection 2025 Jul 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40585354 Free PMC article.
-
Computational approaches for identifying neuropeptides: A comprehensive review.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Nov 28;36(1):102409. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102409. eCollection 2025 Mar 11. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 40171446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Egh16-like virulence factor TrsA of the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys flagrans facilitates intrusion into its host Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Aug 25;21(8):e1013370. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013370. eCollection 2025 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40853931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li C., Kim K. WormBook. 2008. Neuropeptides; pp. 1–36. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

