Impact of the Severity of Reinke's Edema on the Parameters of Voice
- PMID: 38784955
- PMCID: PMC11110086
- DOI: 10.4274/tao.2023.2023-8-10
Impact of the Severity of Reinke's Edema on the Parameters of Voice
Abstract
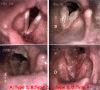
Objective: This study aimed to classify the degree of edema in patients with Reinke's edema (RE) and examine its impact on their voice parameters using both objective and subjective assessment methods.
Methods: Objective and subjective voice data of 104 patients diagnosed with RE between 2018 and 2021 were evaluated retrospectively. RE is classified into 4 groups (types 1, 2, 3, and 4). The evaluation included videolaryngostroboscopic examination, acoustic voice analysis, and aerodynamic measurements, GRBAS, Voice Handicap Index-10 (VHI-10), Voice-Related Quality of Life Scale (V-RQOL), and Reflux Septum Index (RSI).
Results: Patients with type 1 RE had a significantly lower mean age than those with types 3-4. Although there were no significant differences in acoustic and aerodynamic parameters between the groups, it was observed that F0 and the maximum phonation time decreased as the degree of edema increased. The GRBASTotal, G, and R scores of types 1 and 2 were significantly lower than those of types 3 and 4, as were the scores of type 1 S. There were no statistically significant differences between the RE groups in terms of VHI-10, V-RQOL, and RSI scores.
Conclusion: It has been observed that as the severity of RE increases, voice perception and quality (especially types 3 and 4) are negatively affected. Determining the degree of edema will guide the clinician in both the planning of the intervention phase and the follow-up phase.
Keywords: Larynx; Reinke’s edema; classification; dysphonia; laryngology; vocal fold; voice quality.
©Copyright 2023 by Turkish Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Society / Turkish Archives of Otorhinolaryngology is published by Galenos Publishing House.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Similar articles
-
Voice analysis of patients with diverse types of Reinke's edema and clinical use of electroglottographic measurements.Acta Otolaryngol. 2006 Jan;126(1):62-9. doi: 10.1080/00016480510043927. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006. PMID: 16308257
-
Unsedated Office-Based Blue Laser Therapy in Female Patients With Reinke's Edema: A Retrospective Review of 8 Cases.J Voice. 2025 Mar;39(2):525-530. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2022.08.025. Epub 2022 Oct 9. J Voice. 2025. PMID: 36220740
-
Office-based blue laser therapy for vocal fold polyps and Reinke's edema: a case study and review of the literature.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Apr;281(4):1849-1856. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08414-x. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38170211 Review.
-
Reinke's Edema: New Insights into Voice Analysis, a Retrospective Study.J Voice. 2023 Sep 14:S0892-1997(23)00249-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2023.08.008. Online ahead of print. J Voice. 2023. PMID: 37716890
-
Surgical and Nonsurgical Lines of Treatment of Reinke's Edema: A Systematic Literature Review.J Voice. 2021 May;35(3):502.e1-502.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2019.10.016. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Voice. 2021. PMID: 31761692
Cited by
-
Reinke's Oedema in Africa: A Scoping Review.Cureus. 2025 Feb 13;17(2):e78931. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78931. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40091966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tan M, Bryson PC, Pitts C, Woo P, Benninger MS. Clinical grading of Reinke’s edema. Laryngoscope. 2017;127:2310–3. - PubMed
-
- Hah JH, Sim S, An SY, Sung MW, Choi HG. Evaluation of the prevalence of and factors associated with laryngeal diseases among the general population. Laryngoscope. 2015;125:2536–42. - PubMed
-
- de Vincentiis M, Ralli M, Cialente F, Greco A, Marcotullio D, Minni A, et al. Reinke’s edema: a proposal for a classification based on morphological characteristics. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;277:2279–83. - PubMed
-
- Tavaluc R, Tan-Geller M. Reinke’s edema. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2019;52:627–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources