Endothelin and the tumor microenvironment: a finger in every pie
- PMID: 38785410
- PMCID: PMC11130555
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20240426
Endothelin and the tumor microenvironment: a finger in every pie
Abstract
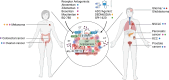
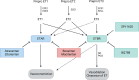
The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a central role in the development of cancer. Within this complex milieu, the endothelin (ET) system plays a key role by triggering epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, causing degradation of the extracellular matrix and modulating hypoxia response, cell proliferation, composition, and activation. These multiple effects of the ET system on cancer progression have prompted numerous preclinical studies targeting the ET system with promising results, leading to considerable optimism for subsequent clinical trials. However, these clinical trials have not lived up to the high expectations; in fact, the clinical trials have failed to demonstrate any substantiated benefit of targeting the ET system in cancer patients. This review discusses the major and recent advances of the ET system with respect to TME and comments on past and ongoing clinical trials of the ET system.
Keywords: Cancer; endothelin; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; hypoxia; tumor microenvironment.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Bagnato A., Tecce R., Moretti C., Di Castro V., Spergel D. and Catt K.J. (1995) Autocrine actions of endothelin-1 as a growth factor in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 1, 1059–1066 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

