A Novel Approach Using Reduced Graphene Oxide for the Detection of ALP and RUNX2 Osteogenic Biomarkers
- PMID: 38785540
- PMCID: PMC11119758
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46050272
A Novel Approach Using Reduced Graphene Oxide for the Detection of ALP and RUNX2 Osteogenic Biomarkers
Abstract
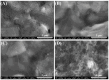
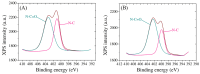
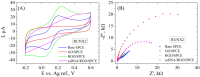
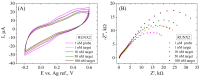
In this work, we propose a new technique involving the modification of commercial screen-printed carbon electrodes with electrochemically reduced graphene oxide to serve as the starting point of a future electrochemical biosensor for the detection of two osteogenic biomarkers: alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2). The electrodes were characterized after each modification by cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, showing the appropriate electrochemical characteristics for each modification type. The results obtained from scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and contact angle measurements are well correlated with each other, demonstrating the successful modification of the electrodes with graphene oxide and its subsequent reduction. The bioreceptors were immobilized on the electrodes by physical adsorption, which was confirmed by electrochemical methods, structural characterization, and contact angle measurements. Finally, the functionalized electrodes were incubated with the specific target analytes and the detection relied on monitoring the electrochemical changes occurring after the hybridization process. Our results indicated that the pilot platform has the ability to detect the two biomarkers up to 1 nM, with increased sensitivity observed for RUNX2, suggesting that after further optimizations, it has a high potential to be employed as a future biosensor.
Keywords: ALP; RUNX2; electrochemistry; electrode modification; osteogenic biomarkers; reduced graphene oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Influence of Graphene Oxide Concentration when Fabricating an Electrochemical Biosensor for DNA Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2019 Sep 26;9(4):113. doi: 10.3390/bios9040113. Biosensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31561443 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Detection Platform Based on RGO Functionalized with Diazonium Salt for DNA Hybridization.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;12(1):39. doi: 10.3390/bios12010039. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35049667 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical immunosensor for botulinum neurotoxin type-E using covalently ordered graphene nanosheets modified electrodes and gold nanoparticles-enzyme conjugate.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Jul 15;69:249-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.02.039. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25754919
-
Self-assembly of glucose oxidase on reduced graphene oxide-magnetic nanoparticles nanocomposite-based direct electrochemistry for reagentless glucose biosensor.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017 Jul 1;76:398-405. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.031. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 28482543
-
Label-Free DNA Biosensor Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide and Gold Nanoparticles.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 8;13(8):797. doi: 10.3390/bios13080797. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622883 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

