Exploring Aggressive Behaviors in Greek Secondary Schools: Prevalence, Sociodemographic Factors, and Comparative Analysis with Elementary School Students
- PMID: 38785896
- PMCID: PMC11117743
- DOI: 10.3390/bs14050405
Exploring Aggressive Behaviors in Greek Secondary Schools: Prevalence, Sociodemographic Factors, and Comparative Analysis with Elementary School Students
Abstract
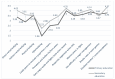
The main objectives of this study are to determine the prevalence of bullying in Greek secondary schools and detect the possible characteristics of bullies' profiles in Greek school settings. A structured questionnaire was given to one hundred ninety-two (n = 192) educators at Greek junior high schools in urban and rural areas. The educators were asked to report the frequencies and forms of aggressive behavior observed during the 2022-2023 school year, the bullies' sociodemographic characteristics, and ways of dealing with bullying episodes. The data are presented, after conducting statistical analyses, in comparison with data for elementary school students. The results revealed that higher rates of bullying were reported compared with elementary school children. Moreover, according to teachers' observations, aggressive behavior is independent of a pupil's diagnosis, but specific types are correlated significantly with a pupil's gender, nationality, low academic performance, and popularity. Factor analysis showed two main factors of aggression types, where common points and differences with elementary school students are mentioned. Implementations for the prevention of school bullying are discussed.
Keywords: Greek schools; aggression; school bullying; school violence; secondary schools; teachers’ perspective.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Álvarez-García D., García T., Núñez J.C. Predictors of school bullying perpetration in adolescence: A systematic review. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2015;23:126–136. doi: 10.1016/j.avb.2015.05.007. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources