The Association between Cyberbullying Victimization and Depression among Children: A Moderated Mediation Model
- PMID: 38785904
- PMCID: PMC11118989
- DOI: 10.3390/bs14050414
The Association between Cyberbullying Victimization and Depression among Children: A Moderated Mediation Model
Abstract
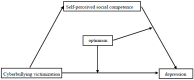
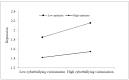
Cyberbullying victimization is becoming more prevalent and adversely affects mental health. This research explores the relationship between the two variables and the underlying mechanism, especially for children, as the impact of mental health in childhood might last a lifetime. Primary school students (N = 344; Mage = 9.90; 43.90% girls) completed self-report questionnaires regarding cyberbullying victimization, self-perceived social competence, optimism, and depression at school. Gender and grade were controlled as covariates. Depression was positively predicted by cyberbullying victimization, while self-perceived social competence played a partially mediating role. In addition, optimism directly and indirectly moderated the effects of cyberbullying victimization on depression. Specifically, the effects were stronger for children with low levels of optimism. Therefore, efforts to enhance children's self-perceived social competence and optimism may reduce their depression resulting from cyberbullying victimization.
Keywords: children; cyberbullying victimization; depression; optimism; self-perceived social competence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that they have no competing or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Longitudinal Relationship between Cyberbullying Victimization and Loneliness among Chinese Middle School Students: The Mediating Effect of Perceived Social Support and the Moderating Effect of Sense of Hope.Behav Sci (Basel). 2024 Apr 11;14(4):312. doi: 10.3390/bs14040312. Behav Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667108 Free PMC article.
-
Positive youth development attributes and cyberbullying victimization among Chinese middle school students: A longitudinal moderated mediation model involving internet gaming disorder and depression.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 30;18(6):e0287729. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287729. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37390070 Free PMC article.
-
The Associations among Cyberbullying Victimization and Chinese and American Adolescents' Mental Health Issues: The Protective Role of Perceived Parental and Friend Support.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Aug 15;21(8):1069. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21081069. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39200678 Free PMC article.
-
Bullying Victimization and Developmental Trajectories of Internalizing and Externalizing Problems: The Moderating Role of Locus of Control Among Children.Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2021 Mar;49(3):351-366. doi: 10.1007/s10802-020-00752-2. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2021. PMID: 33404945 Review.
-
Cyberbullying Victimization and Mental Health Symptoms Among Children and Adolescents: A Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies.Trauma Violence Abuse. 2025 Jan 19:15248380241313051. doi: 10.1177/15248380241313051. Online ahead of print. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2025. PMID: 39828926 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Social Media on Children's Mental Health: A Systematic Scoping Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Nov 28;12(23):2391. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12232391. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39685013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cybulski L., Ashcroft D.M., Carr M.J., Garg S., Chew-Graham C.A., Kapur N., Webb R.T. Temporal trends in annual incidence rates for psychiatric disorders and self-harm among children and adolescents in the UK, 2003–2018. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21:229. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03235-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2021-04-003-BZPK01/Research Program Funds of the Collaborative Innovation Center of Assessment toward Basic Education Quality at Beijing Normal University in China
- SEI-QXZ-2022-016/Research Grants for Young Scholars of Sunglory Education Institute
- 2022011/Research Funds for Young Scholars of Zhejiang Disability Welfare Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources