Functional Genomics and Insights into the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Psoriasis
- PMID: 38785955
- PMCID: PMC11117854
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14050548
Functional Genomics and Insights into the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Psoriasis
Abstract
Psoriasis is a lifelong, systemic, immune mediated inflammatory skin condition, affecting 1-3% of the world's population, with an impact on quality of life similar to diseases like cancer or diabetes. Genetics are the single largest risk factor in psoriasis, with Genome-Wide Association (GWAS) studies showing that many psoriasis risk genes lie along the IL-23/Th17 axis. Potential psoriasis risk genes determined through GWAS can be annotated and characterised using functional genomics, allowing the identification of novel drug targets and the repurposing of existing drugs. This review is focused on the IL-23/Th17 axis, providing an insight into key cell types, cytokines, and intracellular signaling pathways involved. This includes examination of currently available biological treatments, time to relapse post drug withdrawal, and rates of primary/secondary drug failure, showing the need for greater understanding of the underlying genetic mechanisms of psoriasis and how they can impact treatment. This could allow for patient stratification towards the treatment most likely to reduce the burden of disease for the longest period possible.
Keywords: functional genomics; genetics; pathogenesis; psoriasis; tailored medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
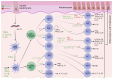
Similar articles
-
Insights into interplay of immunopathophysiological events and molecular mechanistic cascades in psoriasis and its associated comorbidities.J Autoimmun. 2021 Mar;118:102614. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102614. Epub 2021 Feb 9. J Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33578119 Review.
-
[Enlightenment from genome-wide association study to genetics of psoriasis].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009 Jul;38(4):333-7. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009. PMID: 19693967 Chinese.
-
Deciphering the mechanism of Fang-Ji-Di-Huang-Decoction in ameliorating psoriasis-like skin inflammation via the inhibition of IL-23/Th17 cell axis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Dec 5;281:114571. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114571. Epub 2021 Aug 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34464701
-
Combined effect of five single nucleotide polymorphisms related to IL23/Th17 pathway in the risk of psoriasis.Immunogenetics. 2014 Mar;66(3):215-8. doi: 10.1007/s00251-013-0756-z. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Immunogenetics. 2014. PMID: 24419661
-
Role of IL-23 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: a novel potential therapeutic target?Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 May;18(5):513-25. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.889686. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 24568095 Review.
Cited by
-
Persistent reduction of Bifidobacterium longum in the infant gut microbiome in the first year of age following intrapartum penicillin prophylaxis for maternal GBS colonization.Front Immunol. 2025 May 15;16:1540979. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1540979. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40443663 Free PMC article.
-
zDHHC-Mediated S-Palmitoylation in Skin Health and Its Targeting as a Treatment Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 15;26(4):1673. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041673. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psoriasis: Immunological and genetic blueprints driving pathogenesis and potential for personalized therapies.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(6):680-690. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.85335.18442. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40343299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Report on Psoriasis. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

