Molecular Evolution of RAMOSA1 (RA1) in Land Plants
- PMID: 38785957
- PMCID: PMC11117814
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14050550
Molecular Evolution of RAMOSA1 (RA1) in Land Plants
Abstract
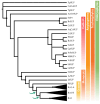
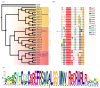
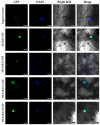
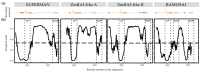
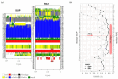
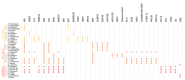
RAMOSA1 (RA1) is a Cys2-His2-type (C2H2) zinc finger transcription factor that controls plant meristem fate and identity and has played an important role in maize domestication. Despite its importance, the origin of RA1 is unknown, and the evolution in plants is only partially understood. In this paper, we present a well-resolved phylogeny based on 73 amino acid sequences from 48 embryophyte species. The recovered tree topology indicates that, during grass evolution, RA1 arose from two consecutive SUPERMAN duplications, resulting in three distinct grass sequence lineages: RA1-like A, RA1-like B, and RA1; however, most of these copies have unknown functions. Our findings indicate that RA1 and RA1-like play roles in the nucleus despite lacking a traditional nuclear localization signal. Here, we report that copies diversified their coding region and, with it, their protein structure, suggesting different patterns of DNA binding and protein-protein interaction. In addition, each of the retained copies diversified regulatory elements along their promoter regions, indicating differences in their upstream regulation. Taken together, the evidence indicates that the RA1 and RA1-like gene families in grasses underwent subfunctionalization and neofunctionalization enabled by gene duplication.
Keywords: collinearity; divergent motifs; embryophyte; nuclear localization; paralogs; phylogeny; promoter; secondary structure; zinc finger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The control of axillary meristem fate in the maize ramosa pathway.Development. 2010 Sep 1;137(17):2849-56. doi: 10.1242/dev.051748. Development. 2010. PMID: 20699296 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of selection at the ramosa1 locus during maize domestication.Mol Ecol. 2010 Apr;19(7):1296-311. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04562.x. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Mol Ecol. 2010. PMID: 20196812
-
Interspecies transfer of RAMOSA1 orthologs and promoter cis sequences impacts maize inflorescence architecture.Plant Physiol. 2023 Feb 12;191(2):1084-1101. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac559. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36508348 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary origin of phytochrome responses and signaling in land plants.Plant Cell Environ. 2017 Nov;40(11):2502-2508. doi: 10.1111/pce.12908. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Plant Cell Environ. 2017. PMID: 28098347 Review.
-
The evolution of land plant cilia.New Phytol. 2012 Aug;195(3):526-540. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04197.x. Epub 2012 Jun 12. New Phytol. 2012. PMID: 22691130 Review.
References
-
- Martienssen R., Vollbrecht E. Nucleotide Sequences Enconding Ramosa 1 Gene and Methods of Use for Same. O1/90343 A2. WO Patent. 2001 November 29;
-
- Yang X. Ph.D. Dissertation. Iowa State University; Ames, IA, USA: 2011. Study of RAMOSA1 Function during Maize Inflorescence Development.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

