The Emerging Role of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 36 (USP36) in Cancer and Beyond
- PMID: 38785979
- PMCID: PMC11118191
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14050572
The Emerging Role of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 36 (USP36) in Cancer and Beyond
Abstract
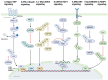
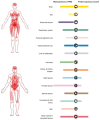
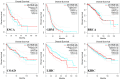
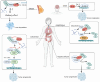
The balance between ubiquitination and deubiquitination is instrumental in the regulation of protein stability and maintenance of cellular homeostasis. The deubiquitinating enzyme, ubiquitin-specific protease 36 (USP36), a member of the USP family, plays a crucial role in this dynamic equilibrium by hydrolyzing and removing ubiquitin chains from target proteins and facilitating their proteasome-dependent degradation. The multifaceted functions of USP36 have been implicated in various disease processes, including cancer, infections, and inflammation, via the modulation of numerous cellular events, including gene transcription regulation, cell cycle regulation, immune responses, signal transduction, tumor growth, and inflammatory processes. The objective of this review is to provide a comprehensive summary of the current state of research on the roles of USP36 in different pathological conditions. By synthesizing the findings from previous studies, we have aimed to increase our understanding of the mechanisms underlying these diseases and identify potential therapeutic targets for their treatment.
Keywords: USP36; cancer; deubiquitinating enzyme; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
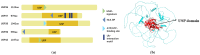

Similar articles
-
The nucleolar ubiquitin-specific protease USP36 deubiquitinates and stabilizes c-Myc.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 24;112(12):3734-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411713112. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25775507 Free PMC article.
-
USP36 inhibits apoptosis by deubiquitinating cIAP1 and survivin in colorectal cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jul;300(7):107463. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107463. Epub 2024 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38876304 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin-specific protease USP36 is a conserved histone H2B deubiquitinase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jan 15;495(3):2363-2368. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.107. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29274341 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of deubiquitinating enzymes in human cancer.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007 Sep;28(9):1325-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00687.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007. PMID: 17723166 Review.
-
Cellular functions, molecular signalings and therapeutic applications: Translational potential of deubiquitylating enzyme USP9X as a drug target in cancer treatment.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 May;1879(3):189099. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189099. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38582329 Review.
Cited by
-
USP1 inhibits influenza A and B virus replication in MDCK cells by mediating RIG-I deubiquitination.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 May 14;82(1):200. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05733-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40369332 Free PMC article.
-
Research advances on signaling pathways regulating the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 31;15:1452078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1452078. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39144141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
USP36 SUMOylates Las1L and Promotes Its Function in Pre-Ribosomal RNA ITS2 Processing.Cancer Res Commun. 2024 Oct 1;4(10):2835-2845. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0312. Cancer Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 39356143 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Multilevel Regulation of EGFR, KRAS, and MYC Oncogenes: Driving Cancer Cell Proliferation Through (Epi)Genetic and Post-Transcriptional/Translational Pathways.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;17(2):248. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020248. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Role of Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme UBE2T in Tumorigenesis: A Comprehensive Review.Cells. 2024 Dec 26;14(1):15. doi: 10.3390/cells14010015. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39791716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

