The Role of FKBPs in Complex Disorders: Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Cancer, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 38786025
- PMCID: PMC11119362
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13100801
The Role of FKBPs in Complex Disorders: Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Cancer, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Stress is a common denominator of complex disorders and the FK-506 binding protein (FKBP)51 plays a central role in stress. Hence, it is not surprising that multiple studies imply the involvement of the FKBP51 protein and/or its coding gene, FKBP5, in complex disorders. This review summarizes such reports concentrating on three disorder clusters-neuropsychiatric, cancer, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We also attempt to point to potential mechanisms suggested to mediate the effect of FKBP5/FKBP51 on these disorders. Neuropsychiatric diseases considered in this paper include (i) Huntington's disease for which increased autophagic cellular clearance mechanisms related to decreased FKBP51 protein levels or activity is discussed, Alzheimer's disease for which increased FKBP51 activity has been shown to induce Tau phosphorylation and aggregation, and Parkinson's disease in the context of which FKBP12 is mentioned; and (ii) mental disorders, for which significant association with the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1360780 of FKBP5 intron 7 along with decreased DNA methylation were revealed. Since cancer is a large group of diseases that can start in almost any organ or tissue of the body, FKBP51's role depends on the tissue type and differences among pathways expressed in those tumors. The FKBP51-heat-shock protein-(Hsp)90-p23 super-chaperone complex might function as an oncogene or as a tumor suppressor by downregulating the serine/threonine protein kinase (AKt) pathway. In T2DM, two potential pathways for the involvement of FKBP51 are highlighted as affecting the pathogenesis of the disease-the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and AKt.
Keywords: FKBP5; cancer; complex disorders; neuropsychiatric disorders; type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures
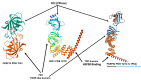
 A mouse model of PD.
A mouse model of PD.  mRNA.
mRNA.  DNA.
DNA.  Fast proliferating cells (cancer).
Fast proliferating cells (cancer).  Over-expression of the chaperone complex consisting of FKBP51 and HSP90.
Over-expression of the chaperone complex consisting of FKBP51 and HSP90.  Inhibition.
Inhibition.  Aggregation of mutant Tau.
Aggregation of mutant Tau.References
-
- Wu B., Li P., Liu Y., Lou Z., Ding Y., Shu C., Ye S., Bartlam M., Shen B., Rao Z. 3D structure of human FK506-binding protein 52: Implications for the assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor/Hsp90/immunophilin heterocomplex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:8348–8353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0305969101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

