Senotherapeutic Peptide 14 Suppresses Th1 and M1 Human T Cell and Monocyte Subsets In Vitro
- PMID: 38786036
- PMCID: PMC11120033
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13100813
Senotherapeutic Peptide 14 Suppresses Th1 and M1 Human T Cell and Monocyte Subsets In Vitro
Abstract
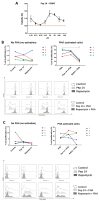
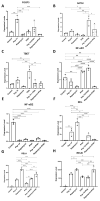
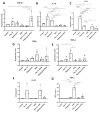
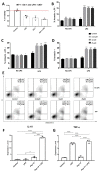
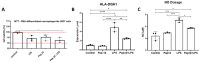
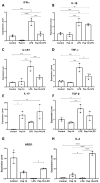
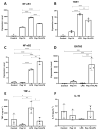
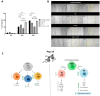
Inflammation contributes to the onset and exacerbation of numerous age-related diseases, often manifesting as a chronic condition during aging. Given that cellular senescence fosters local and systemic inflammation, senotherapeutic interventions could potentially aid in managing or even reducing inflammation. Here, we investigated the immunomodulatory effects of the senotherapeutic Peptide 14 (Pep 14) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), monocytes, and macrophages. We found that, despite failing to significantly influence T cell activation and proliferation, the peptide promoted a Th2/Treg gene expression and cytokine signature in PBMCs, characterized by increased expression of the transcription factors GATA3 and FOXP3, as well as the cytokines IL-4 and IL-10. These observations were partially confirmed through ELISA, in which we observed increased IL-10 release by resting and PHA-stimulated PBMCs. In monocytes from the U-937 cell line, Pep 14 induced apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated cells and upregulated IL-10 expression. Furthermore, Pep 14 prevented LPS-induced activation and promoted an M2-like polarization in U-937-derived macrophages, evidenced by decreased expression of M1 markers and increased expression of M2 markers. We also showed that the conditioned media from Pep 14-treated macrophages enhanced fibroblast migration, indicative of a functional M2 phenotype. Taken together, our findings suggest that Pep 14 modulates immune cell function towards an anti-inflammatory and regenerative phenotype, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic intervention to alleviate immunosenescence-associated dysregulation.
Keywords: aging; immunomodulation; inflammaging; multifunctional peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors A.Z., M.B., and J.L.C. are collaborators and/or scientific advisors for OneSkin Technologies. All other authors declare that they have no conflicting interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TLR2 stimulation impairs anti-inflammatory activity of M2-like macrophages, generating a chimeric M1/M2 phenotype.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;19(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1447-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096690 Free PMC article.
-
M2 polarization of murine peritoneal macrophages induces regulatory cytokine production and suppresses T-cell proliferation.Immunology. 2016 Nov;149(3):320-328. doi: 10.1111/imm.12647. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Immunology. 2016. PMID: 27421990 Free PMC article.
-
Human amnion favours tissue repair by inducing the M1-to-M2 switch and enhancing M2 macrophage features.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017 Oct;11(10):2895-2911. doi: 10.1002/term.2193. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017. PMID: 27396853 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous immune globulin affects cytokine production in T lymphocytes and monocytes/macrophages.Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 May;104 Suppl 1:10-20. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8625537
-
Effect of colorectal cancer-derived extracellular vesicles on the immunophenotype and cytokine secretion profile of monocytes and macrophages.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Apr 24;16(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0229-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 29690889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wikby A., Nilsson B.-O., Forsey R., Thompson J., Strindhall J., Löfgren S., Ernerudh J., Pawelec G., Ferguson F., Johansson B. The immune risk phenotype is associated with IL-6 in the terminal decline stage: Findings from the Swedish NONA immune longitudinal study of very late life functioning. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2006;127:695–704. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2006.04.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 0001/Universidade Católica de Brasília
- 0001/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 0001/Foundation for Research Support of the Federal District
- 0001/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- 0001/Fundação de Apoio ao Desenvolvimento do Ensino, Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Mato Grosso do Sul
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

