Cross-Talks between Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein and Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 Expressions in Cancer: Role in Immune Evasion and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 38786085
- PMCID: PMC11119125
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13100864
Cross-Talks between Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein and Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 Expressions in Cancer: Role in Immune Evasion and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
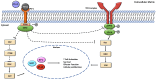
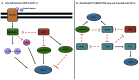
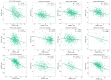
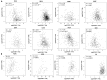
Innovations in cancer immunotherapy have resulted in the development of several novel immunotherapeutic strategies that can disrupt immunosuppression. One key advancement lies in immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), which have shown significant clinical efficacy and increased survival rates in patients with various therapy-resistant cancers. This immune intervention consists of monoclonal antibodies directed against inhibitory receptors (e.g., PD-1) on cytotoxic CD8 T cells or against corresponding ligands (e.g., PD-L1/PD-L2) overexpressed on cancer cells and other cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME). However, not all cancer cells respond-there are still poor clinical responses, immune-related adverse effects, adaptive resistance, and vulnerability to ICIs in a subset of patients with cancer. This challenge showcases the heterogeneity of cancer, emphasizing the existence of additional immunoregulatory mechanisms in many patients. Therefore, it is essential to investigate PD-L1's interaction with other oncogenic genes and pathways to further advance targeted therapies and address resistance mechanisms. Accordingly, our aim was to investigate the mechanisms governing PD-L1 expression in tumor cells, given its correlation with immune evasion, to uncover novel mechanisms for decreasing PD-L1 expression and restoring anti-tumor immune responses. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the upregulation of Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein (RKIP) in many cancers contributes to the suppression of key hyperactive pathways observed in malignant cells, alongside its broadening involvement in immune responses and the modulation of the TME. We, therefore, hypothesized that the role of PD-L1 in cancer immune surveillance may be inversely correlated with the low expression level of the tumor suppressor Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein (RKIP) expression in cancer cells. This hypothesis was investigated and we found several signaling cross-talk pathways between the regulations of both RKIP and PD-L1 expressions. These pathways and regulatory factors include the MAPK and JAK/STAT pathways, GSK3β, cytokines IFN-γ and IL-1β, Sox2, and transcription factors YY1 and NFκB. The pathways that upregulated PD-L1 were inhibitory for RKIP expression and vice versa. Bioinformatic analyses in various human cancers demonstrated the inverse relationship between PD-L1 and RKIP expressions and their prognostic roles. Therefore, we suspect that the direct upregulation of RKIP and/or the use of targeted RKIP inducers in combination with ICIs could result in a more targeted anti-tumor immune response-addressing the therapeutic challenges related to PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy alone.
Keywords: PD-L1; RKIP; cancer; cross-talk; immune evasion; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
YY1 regulates cancer cell immune resistance by modulating PD-L1 expression.Drug Resist Updat. 2019 Mar;43:10-28. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Drug Resist Updat. 2019. PMID: 31005030 Review.
-
Inverse correlation between the metastasis suppressor RKIP and the metastasis inducer YY1: Contrasting roles in the regulation of chemo/immuno-resistance in cancer.Drug Resist Updat. 2017 Jan;30:28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Drug Resist Updat. 2017. PMID: 28363333 Review.
-
What Do We Have to Know about PD-L1 Expression in Prostate Cancer? A Systematic Literature Review. Part 3: PD-L1, Intracellular Signaling Pathways and Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 15;22(22):12330. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212330. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830209 Free PMC article.
-
Augmenting Anticancer Immunity Through Combined Targeting of Angiogenic and PD-1/PD-L1 Pathways: Challenges and Opportunities.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 5;11:598877. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.598877. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33250900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Communication between EMT and PD-L1 signaling: New insights into tumor immune evasion.Cancer Lett. 2020 Jan 1;468:72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.013. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31605776 Review.
Cited by
-
From Bench to Bedside in Emerging Therapies for Gynecological Malignancies: A Narrative Review.Cancer Control. 2025 Jan-Dec;32:10732748251357158. doi: 10.1177/10732748251357158. Epub 2025 Jul 6. Cancer Control. 2025. PMID: 40619274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Glioblastoma Enigma: Exploring PD-L1 (Programmed Death-Ligand 1) and IDH1 (Isocitrate Dehydrogenase-1) Expression and Their Immunotherapeutic Implications.Cureus. 2025 Jan 4;17(1):e76920. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76920. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39906459 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical or non-canonical, all aspects of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in heart failure.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2025 Mar;241(3):e70010. doi: 10.1111/apha.70010. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 39960030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

