Subcellular Feature-Based Classification of α and β Cells Using Soft X-ray Tomography
- PMID: 38786091
- PMCID: PMC11119489
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13100869
Subcellular Feature-Based Classification of α and β Cells Using Soft X-ray Tomography
Abstract
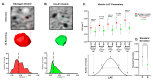
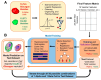
The dysfunction of α and β cells in pancreatic islets can lead to diabetes. Many questions remain on the subcellular organization of islet cells during the progression of disease. Existing three-dimensional cellular mapping approaches face challenges such as time-intensive sample sectioning and subjective cellular identification. To address these challenges, we have developed a subcellular feature-based classification approach, which allows us to identify α and β cells and quantify their subcellular structural characteristics using soft X-ray tomography (SXT). We observed significant differences in whole-cell morphological and organelle statistics between the two cell types. Additionally, we characterize subtle biophysical differences between individual insulin and glucagon vesicles by analyzing vesicle size and molecular density distributions, which were not previously possible using other methods. These sub-vesicular parameters enable us to predict cell types systematically using supervised machine learning. We also visualize distinct vesicle and cell subtypes using Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) embeddings, which provides us with an innovative approach to explore structural heterogeneity in islet cells. This methodology presents an innovative approach for tracking biologically meaningful heterogeneity in cells that can be applied to any cellular system.
Keywords: 3D cell mapping; Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP); cryogenic fluorescence microscopy; machine learning; pancreatic islets; soft X-ray tomography; α cells; β cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterizing pancreatic β-cell heterogeneity in the streptozotocin model by single-cell transcriptomic analysis.Mol Metab. 2020 Jul;37:100982. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.100982. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32247924 Free PMC article.
-
Soft X-ray tomography to map and quantify organelle interactions at the mesoscale.Structure. 2022 Apr 7;30(4):510-521.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2022.01.006. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Structure. 2022. PMID: 35148829 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Alpha-Cells Contribute Together With Beta-Cells to CXCL10 Expression in Type 1 Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Sep 15;11:630. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00630. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33042009 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic α-cells - The unsung heroes in islet function.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul;103:41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.01.006. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 31983511 Review.
-
Single-Cell RNA-Seq of the Pancreatic Islets--a Promise Not yet Fulfilled?Cell Metab. 2019 Mar 5;29(3):539-544. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.11.016. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 30581120 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Montet X., Lamprianou S., Vinet L., Meda P., Fort A. Islets of Langerhans. 2nd ed. Springer Netherlands; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2014. Approaches for Imaging Pancreatic Islets: Recent Advances and Future Prospects; pp. 1–21.
-
- Wang Z., Gurlo T., Matveyenko A.V., Elashoff D., Wang P., Rosenberger M., Junge J.A., Stevens R.C., White K.L., Fraser S.E., et al. Live-Cell Imaging of Glucose-Induced Metabolic Coupling of β and α Cell Metabolism in Health and Type 2 Diabetes. Commun. Biol. 2021;4:594. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02113-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

