Modification of Gas6 Protein in the Brain by a Functional Endogenous Tissue Vitamin K Cycle
- PMID: 38786095
- PMCID: PMC11119062
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13100873
Modification of Gas6 Protein in the Brain by a Functional Endogenous Tissue Vitamin K Cycle
Abstract
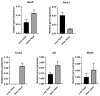
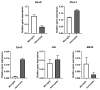
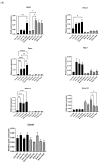
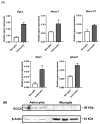
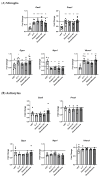
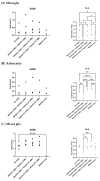
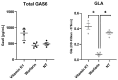
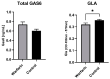
The TAM receptor ligand Gas6 is known for regulating inflammatory and immune pathways in various organs including the brain. Gas6 becomes fully functional through the post-translational modification of multiple glutamic acid residues into γ-carboxyglutamic in a vitamin K-dependent manner. However, the significance of this mechanism in the brain is not known. We report here the endogenous expression of multiple components of the vitamin K cycle within the mouse brain at various ages as well as in distinct brain glial cells. The brain expression of all genes was increased in the postnatal ages, mirroring their profiles in the liver. In microglia, the proinflammatory agent lipopolysaccharide caused the downregulation of all key vitamin K cycle genes. A secreted Gas6 protein was detected in the medium of both mouse cerebellar slices and brain glial cell cultures. Furthermore, the endogenous Gas6 γ-carboxylation level was abolished through incubation with the vitamin K antagonist warfarin and could be restored through co-incubation with vitamin K1. Finally, the γ-carboxylation level of the Gas6 protein within the brains of warfarin-treated rats was found to be significantly reduced ex vivo compared to the control brains. In conclusion, we demonstrated for the first time the existence of a functional vitamin K cycle within rodent brains, which regulates the functional modification of endogenous brain Gas6. These results indicate that vitamin K is an important nutrient for the brain. Furthermore, the measurement of vitamin K-dependent Gas6 functionality could be an indicator of homeostatic or disease mechanisms in the brain, such as in neurological disorders where Gas6/TAM signalling is impaired.
Keywords: Gas6; TAM receptor; glia; microglia; neurodegenerative disease; neuroinflammation; nutrition; vitamin K; warfarin; γ-carboxyglutamic acid; γ-carboxylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Requirement of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues for the biological activity of Gas6: contribution of endogenous Gas6 to the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells.Biochem J. 1997 Apr 15;323 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):387-92. doi: 10.1042/bj3230387. Biochem J. 1997. PMID: 9163328 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin K-dependent Gas6 activates ERK kinase and stimulates growth of cardiac fibroblasts.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Jul 2;319(3):871-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.070. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15184064
-
Gas6/TAM Signalling Negatively Regulates Inflammatory Induction of GM-CSF in Mouse Brain Microglia.Cells. 2021 Nov 24;10(12):3281. doi: 10.3390/cells10123281. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943789 Free PMC article.
-
[Gas-6 and protein S: vitamin K-dependent factors and ligands for the TAM tyrosine kinase receptors family].Med Sci (Paris). 2007 Oct;23(10):826-33. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20072310826. Med Sci (Paris). 2007. PMID: 17937890 Review. French.
-
Growth arrest-specific gene 6 (GAS6). An outline of its role in haemostasis and inflammation.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Oct;100(4):604-10. doi: 10.1160/th08-04-0253. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18841281 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin K and women's health: a review.Front Glob Womens Health. 2025 Jul 11;6:1590414. doi: 10.3389/fgwh.2025.1590414. eCollection 2025. Front Glob Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40718363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin K1 Administration Increases the Level of Circulating Carboxylated Osteocalcin in Critically Ill Patients.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 19;17(2):348. doi: 10.3390/nu17020348. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39861478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goruppi S., Ruaro E., Schneider C. Gas6, the Ligand of Axl Tyrosine Kinase Receptor, Has Mitogenic and Survival Activities for Serum Starved NIH3T3 Fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1996;12:471–480. - PubMed
-
- Angelillo-Scherrer A., Burnier L., Flores N., Savi P., DeMol M., Schaeffer P., Herbert J.-M., Lemke G., Goff S.P., Matsushima G.K., et al. Role of Gas6 Receptors in Platelet Signaling during Thrombus Stabilization and Implications for Antithrombotic Therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2005;115:237–246. doi: 10.1172/JCI22079. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

