Characterization of Salmonella Phage P1-CTX and the Potential Mechanism Underlying the Acquisition of the blaCTX-M-27 Gene
- PMID: 38786174
- PMCID: PMC11117986
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13050446
Characterization of Salmonella Phage P1-CTX and the Potential Mechanism Underlying the Acquisition of the blaCTX-M-27 Gene
Abstract
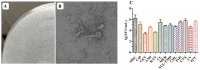
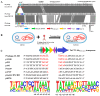
The P1 phage has garnered attention as a carrier of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in Enterobacteriaceae. However, the transferability of ARGs by P1-like phages carrying ARGs, in addition to the mechanism underlying ARG acquisition, remain largely unknown. In this study, we elucidated the biological characteristics, the induction and transmission abilities, and the acquisition mechanism of the blaCTX-M-27 gene in the P1 phage. The P1-CTX phage exhibited distinct lytic plaques and possessed a complete head and tail structure. Additionally, the P1-CTX phage was induced successfully under various conditions, including UV exposure, heat treatment at 42 °C, and subinhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs) of antibiotics. Moreover, the P1-CTX phage could mobilize the blaCTX-M-27 gene into three strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli) and the following seven different serotypes of Salmonella: Rissen, Derby, Kentucky, Typhimurium, Cerro, Senftenberg, and Muenster. The mechanism underlying ARG acquisition by the P1-CTX phage involved Tn1721 transposition-mediated movement of blaCTX-M-27 into the ref and mat genes within its genome. To our knowledge, this is the first report documenting the dynamic processes of ARG acquisition by a phage. Furthermore, this study enriches the research on the mechanism underlying the phage acquisition of drug resistance genes and provides a basis for determining the risk of drug resistance during phage transmission.
Keywords: P1-CTX phage; Salmonella; acquisition mechanism; blaCTX-M-27.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mobilization of Tn1721-like structure harboring blaCTX-M-27 between P1-like bacteriophage in Salmonella and plasmids in Escherichia coli in China.Vet Microbiol. 2021 Feb;253:108944. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108944. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Vet Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33370618
-
Characterization of a P1-like bacteriophage carrying CTX-M-27 in Salmonella spp. resistant to third generation cephalosporins isolated from pork in China.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 18;7:40710. doi: 10.1038/srep40710. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28098241 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance genes in phage particles isolated from human faeces and induced from clinical bacterial isolates.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018 Mar;51(3):434-442. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.11.014. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018. PMID: 29180282
-
Similarities of P1-Like Phage Plasmids and Their Role in the Dissemination of blaCTX-M-55.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0141022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01410-22. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36069562 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Chromosomally Located blaCTX-M-55 in Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 Isolates Recovered from a Tertiary Hospital in Guangzhou, China.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0277121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02771-21. Epub 2022 May 26. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35616373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birgy A., Levy C., Nicolas-Chanoine M.H., Cointe A., Hobson C.A., Magnan M., Bechet S., Bidet P., Cohen R., Bonacorsi S. Independent Host Factors and Bacterial Genetic Determinants of the Emergence and Dominance of Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 CTX-M-27 in a Community Pediatric Cohort Study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019;63:e00382-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00382-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

