Role of Cefiderocol in Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Central Nervous System Infections: Real Life Experience and State-of-the-Art
- PMID: 38786181
- PMCID: PMC11118811
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13050453
Role of Cefiderocol in Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Central Nervous System Infections: Real Life Experience and State-of-the-Art
Abstract
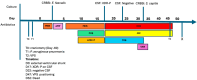
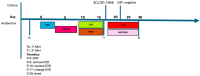
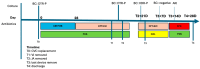
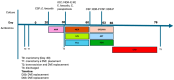
Cefiderocol is a new molecule effective against multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative pathogens. Currently, there is limited evidence regarding the use of cefiderocol in central nervous system (CNS) infections. Data on the cerebrospinal fluid penetration rate of cefiderocol are limited and heterogeneous, and there is no consensus on the dosing scheme of cefiderocol to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. We present a case series and a literature review of CNS infections caused by MDR pathogens that were treated with cefiderocol: some of these patients were treated with different dose schemes of cefiderocol and underwent therapeutic drug monitoring both on plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The CSF penetration rates and the clinical outcomes were evaluated.
Keywords: CNS infections; cefiderocol; central nervous system; gram-negative; neurosurgical device infections; therapeutic drug monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhanel G.G., Golden A.R., Zelenitsky S., Wiebe K., Lawrence C.K., Adam H.J., Idowu T., Domalaon R., Schweizer F., Zhanel M.A., et al. Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli. Drugs. 2019;79:271–289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bakdach D., Elajez R., Bakdach A.R., Awaisu A., De Pascale G., Ait Hssain A. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Dosing Considerations of Novel β-Lactams and β-Lactam/β-Lactamase Inhibitors in Critically Ill Adult Patients: Focus on Obesity, Augmented Renal Clearance, Renal Replacement Therapies, and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. J. Clin. Med. 2022;11:6898. doi: 10.3390/jcm11236898. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi N., Katsube T., Echols R., Wajima T. Population Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Analyses of Cefiderocol, a Parenteral Siderophore Cephalosporin, in Patients with Pneumonia, Bloodstream Infection/Sepsis, or Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021;65:e01437-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01437-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

