Tuberculous Spondylodiscitis with Psoas Abscess Descending into the Anterior Femoral Compartment Identified Using 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoroglucose Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography
- PMID: 38786316
- PMCID: PMC11119091
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14101018
Tuberculous Spondylodiscitis with Psoas Abscess Descending into the Anterior Femoral Compartment Identified Using 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoroglucose Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography
Abstract
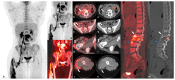
A 24-year-old immunocompetent woman underwent whole-body 18F-FDG PET/CT for the evaluation of MRI-suspicious tuberculous spinal lesions. The PET/CT results showed no pathological uptake in either lung, and there were no pathological changes on CT. There was increased uptake in the right psoas muscle, extending continuously down anterior to the right hip joint, posterior to and around the trochanteric region of the right femur, and into the right thigh, with an SUVmaxbw of 17.0. Subsequently, the patient underwent CT-guided biopsy as per protocol, which revealed drug-sensitive Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and the patient was started on standard tuberculosis treatment for 12 months.
Keywords: PET/CT; Pott’s disease; drug-sensitive; psoas abscess; tuberculous spondylodiscitis.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has a relationship with industry or financial disclosure related to the content of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multi-level tuberculosis of the spine identified by 18 F-FDG-PET/CT and concomitant urogenital tuberculosis: a case report from the spinal TB X cohort.Infection. 2024 Dec;52(6):2507-2519. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02327-5. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Infection. 2024. PMID: 38896371 Free PMC article.
-
Higher fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) uptake in tuberculous compared to bacterial spondylodiscitis.Skeletal Radiol. 2017 Jun;46(6):777-783. doi: 10.1007/s00256-017-2615-8. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Skeletal Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28299432
-
A Case of Pott's Disease Complicated by Tuberculous Meningitis and Psoas Abscess Diagnosed by Computed Tomography-Guided Percutaneous Drainage.Cureus. 2024 Nov 15;16(11):e73750. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73750. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39677164 Free PMC article.
-
A case of skeletal tuberculosis and psoas abscess: disease activity evaluated using (18) F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography.BMC Med Imaging. 2013 Nov 14;13:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-2342-13-37. BMC Med Imaging. 2013. PMID: 24225333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical imaging features of tuberculous spondylitis: case report with literature review.J Radiol Case Rep. 2014 Nov 30;8(11):1-14. doi: 10.3941/jrcr.v8i11.2309. eCollection 2014 Nov. J Radiol Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 25926906 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Primary Iliopsoas Abscess and Drug-Induced Liver Injury in the Emergency Department: A Case Report.Diseases. 2024 Dec 12;12(12):326. doi: 10.3390/diseases12120326. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 39727656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batirel A., Erdem H., Sengoz G., Pehlivanoglu F., Ramosaco E., Gülsün S., Tekin R., Mete B., Balkan I., Sevgi D., et al. The course of spinal tuberculosis (Pott disease): Results of the multinational, multicentre Backbone-2 study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015;21:1008.e9–1008.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.07.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shetty A., Kanna R.M., Rajasekaran S. TB spine—Current aspects on clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management options. Semin. Spine Surg. 2016;28:150–162. doi: 10.1053/j.semss.2015.07.006. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

