Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Unhealthy Lifestyle in Adolescence: Unforeseen Role of Allostatic Overload and Psychological Well-Being
- PMID: 38786368
- PMCID: PMC11121659
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12100956
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Unhealthy Lifestyle in Adolescence: Unforeseen Role of Allostatic Overload and Psychological Well-Being
Abstract
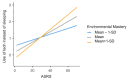
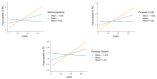
Unhealthy lifestyle behaviors (ULBs) are common in early adolescence and could be worsened by Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), as well as by specific psychosocial factors, such as stress and unbalanced (i.e., too high or low scores of) psychological well-being (PWB) dimensions. This multi-center study aimed to evaluate how interactions between ADHD symptoms and psychosocial factors associated with ULBs (i.e., Allostatic Overload and multidimensional Psychological Well-Being), considered as moderators, could affect the adoption of ULBs during adolescence. A total of 440 fourteen-year-old adolescents were recruited from six upper secondary schools in Bologna and Rome (Italy) and completed self-report questionnaires on ULBs, ADHD, and psychosocial factors. Relations between ADHD symptomatology and specific ULBs (i.e., impaired sleep, problematic Internet use) were moderated by variables deemed as "negative" (i.e., Allostatic Overload) or "positive" (i.e., PWB dimensions of Self-Acceptance, Personal Growth, Positive Relations, Purpose in Life, Environmental Mastery): when the "negative" moderator is absent and the levels of the "positive" moderators are higher, ULBs decrease among students with lower ADHD symptomatology but increase among students with more severe ADHD. Based on ADHD severity, interventions should aim at promoting a state of euthymia, which consists in balanced PWB dimensions and reflects the optimal level of well-being to fulfill one's own potential and self-realization.
Keywords: ADHD; adolescence; allostatic overload; moderation analysis; psychological well-being; unhealthy behaviors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Bener A., Yildirim E., Torun P., Çatan F., Bolat E., Alıç S., Akyel S., Griffiths M.D. Internet addiction, fatigue, and sleep problems among adolescent students: A large-scale study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2019;17:959–969. doi: 10.1007/s11469-018-9937-1. - DOI
-
- Firth J., Solmi M., Wootton R.E., Vancampfort D., Schuch F.B., Hoare E., Gilbody S., Torous J., Teasdale S.B., Jackson S.E., et al. A meta-review of “lifestyle psychiatry”: The role of exercise, smoking, diet and sleep in the prevention and treatment of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2020;19:360–380. doi: 10.1002/wps.20773. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

