Whale Optimization for Cloud-Edge-Offloading Decision-Making for Smart Grid Services
- PMID: 38786512
- PMCID: PMC11118963
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics9050302
Whale Optimization for Cloud-Edge-Offloading Decision-Making for Smart Grid Services
Abstract
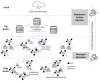
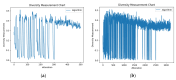
As IoT metering devices become increasingly prevalent, the smart energy grid encounters challenges associated with the transmission of large volumes of data affecting the latency of control services and the secure delivery of energy. Offloading computational work towards the edge is a viable option; however, effectively coordinating service execution on edge nodes presents significant challenges due to the vast search space making it difficult to identify optimal decisions within a limited timeframe. In this research paper, we utilize the whale optimization algorithm to decide and select the optimal edge nodes for executing services' computational tasks. We employ a directed acyclic graph to model dependencies among computational nodes, data network links, smart grid energy assets, and energy network organization, thereby facilitating more efficient navigation within the decision space to identify the optimal solution. The offloading decision variables are represented as a binary vector, which is evaluated using a fitness function considering round-trip time and the correlation between edge-task computational resources. To effectively explore offloading strategies and prevent convergence to suboptimal solutions, we adapt the feedback mechanisms, an inertia weight coefficient, and a nonlinear convergence factor. The evaluation results are promising, demonstrating that the proposed solution can effectively consider both energy and data network constraints while enduring faster decision-making for optimization, with notable improvements in response time and a low average execution time of approximately 0.03 s per iteration. Additionally, on complex computational infrastructures modeled, our solution shows strong features in terms of diversity, fitness evolution, and execution time.
Keywords: cloud–edge offloading; directed acyclic graph; energy efficiency; smart grid; whale optimization algorithm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Kumar S., Tiwari P., Zymbler M. Internet of Things is a revolutionary approach for future technology enhancement: A review. J. Big Data. 2019;6:111. doi: 10.1186/s40537-019-0268-2. - DOI
-
- Wang J., Gao F., Zhou Y., Guo Q., Tan C.-W., Song J., Wang Y. Data sharing in energy systems. Adv. Appl. Energy. 2023;10:100132. doi: 10.1016/j.adapen.2023.100132. - DOI
-
- Lin L., Liao X., Jin H., Li P. Computation Offloading Toward Edge Computing. Proc. IEEE. 2019;107:1584–1607. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2922285. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

