Artificial Intelligence, Intrapartum Ultrasound and Dystocic Delivery: AIDA (Artificial Intelligence Dystocia Algorithm), a Promising Helping Decision Support System
- PMID: 38786561
- PMCID: PMC11122467
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging10050107
Artificial Intelligence, Intrapartum Ultrasound and Dystocic Delivery: AIDA (Artificial Intelligence Dystocia Algorithm), a Promising Helping Decision Support System
Abstract
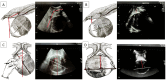
The position of the fetal head during engagement and progression in the birth canal is the primary cause of dystocic labor and arrest of progression, often due to malposition and malrotation. The authors performed an investigation on pregnant women in labor, who all underwent vaginal digital examination by obstetricians and midwives as well as intrapartum ultrasonography to collect four "geometric parameters", measured in all the women. All parameters were measured using artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, called AIDA (artificial intelligence dystocia algorithm), which incorporates a human-in-the-loop approach, that is, to use AI (artificial intelligence) algorithms that prioritize the physician's decision and explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). The AIDA was structured into five classes. After a number of "geometric parameters" were collected, the data obtained from the AIDA analysis were entered into a red, yellow, or green zone, linked to the analysis of the progress of labor. Using the AIDA analysis, we were able to identify five reference classes for patients in labor, each of which had a certain sort of birth outcome. A 100% cesarean birth prediction was made in two of these five classes. The use of artificial intelligence, through the evaluation of certain obstetric parameters in specific decision-making algorithms, allows physicians to systematically understand how the results of the algorithms can be explained. This approach can be useful in evaluating the progress of labor and predicting the labor outcome, including spontaneous, whether operative VD (vaginal delivery) should be attempted, or if ICD (intrapartum cesarean delivery) is preferable or necessary.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; asynclitism; cesarean section; dystocia; intrapartum ultrasound; labor; malposition; malrotation; vaginal operative delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AIDA (Artificial Intelligence Dystocia Algorithm) in Prolonged Dystocic Labor: Focus on Asynclitism Degree.J Imaging. 2024 Aug 9;10(8):194. doi: 10.3390/jimaging10080194. J Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39194983 Free PMC article.
-
Dystocia, Delivery, and Artificial Intelligence in Labor Management: Perspectives and Future Directions.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 25;13(21):6410. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216410. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518549 Free PMC article.
-
Labor progress determined by ultrasound is different in women requiring cesarean delivery from those who experience a vaginal delivery following induction of labor.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Oct;221(4):335.e1-335.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.05.040. Epub 2019 May 30. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 31153931
-
Intrapartum sonography of fetal head in second stage of labor with neuraxial analgesia: a literature review and possible medicolegal aftermath.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Apr;23(8):3159-3166. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201904_17673. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31081066 Review.
-
Asynclitism and Its Ultrasonographic Rediscovery in Labor Room to Date: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;12(12):2998. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12122998. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553005 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AIDA (Artificial Intelligence Dystocia Algorithm) in Prolonged Dystocic Labor: Focus on Asynclitism Degree.J Imaging. 2024 Aug 9;10(8):194. doi: 10.3390/jimaging10080194. J Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39194983 Free PMC article.
-
Dystocia, Delivery, and Artificial Intelligence in Labor Management: Perspectives and Future Directions.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 25;13(21):6410. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216410. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518549 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence Dystocia Algorithm (AIDA) as a Decision Support System in Transverse Fetal Head Position.J Imaging. 2025 Jul 5;11(7):223. doi: 10.3390/jimaging11070223. J Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40710610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nizard J., Haberman S., Paltieli Y., Gonen R., Ohel G., Le Bourthe Y., Ville Y. Determination of fetal head station and position during labor: A new technique that combines ultrasound and a position-tracking system. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009;200:404.e1–404.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2008.10.051. - DOI - PubMed
-
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 154: Operative Vaginal Delivery. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015;126:e56–e65. - PubMed
-
- Dupuis O., Silveira R., Zentner A., Dittmar A., Gaucherand P., Cucherat M., Redarce T., Rudigoz R.C. Birth simulator: Reliability of transvaginal assessment of fetal head station as defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists classification. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005;192:868–874. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.09.028. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

