Antiviral Shrimp lncRNA06 Possesses Anti-Tumor Activity by Inducing Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer Stem Cells in a Cross-Species Manner
- PMID: 38786611
- PMCID: PMC11123040
- DOI: 10.3390/md22050221
Antiviral Shrimp lncRNA06 Possesses Anti-Tumor Activity by Inducing Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer Stem Cells in a Cross-Species Manner
Abstract
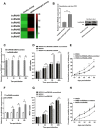
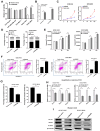
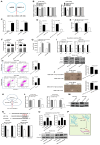
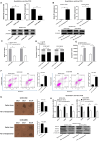
Virus infection causes the metabolic disorder of host cells, whereas the metabolic disorder of cells is one of the major causes of tumorigenesis, suggesting that antiviral molecules might possess anti-tumor activities by regulating cell metabolism. As the key regulators of gene expression, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play vital roles in the regulation of cell metabolism. However, the influence of antiviral lncRNAs on tumorigenesis has not been explored. To address this issue, the antiviral and anti-tumor capacities of shrimp lncRNAs were characterized in this study. The results revealed that shrimp lncRNA06, having antiviral activity in shrimp, could suppress the tumorigenesis of human gastric cancer stem cells (GCSCs) via triggering apoptosis of GCSCs in a cross-species manner. Shrimp lncRNA06 could sponge human miR-17-5p to suppress the stemness of GCSCs via the miR-17-5p-p21 axis. At the same time, shrimp lncRNA06 could bind to ATP synthase subunit beta (ATP5F1B) to enhance the stability of the ATP5F1B protein in GCSCs, thus suppressing the tumorigenesis of GCSCs. The in vivo data demonstrated that shrimp lncRNA06 promoted apoptosis and inhibited the stemness of GCSCs through interactions with ATP5F1B and miR-17-5p, leading to the suppression of the tumorigenesis of GCSCs. Therefore, our findings highlighted that antiviral lncRNAs possessed anti-tumor capacities and that antiviral lncRNAs could be the anti-tumor reservoir for the treatment of human cancers.
Keywords: antiviral lncRNA; cross-species regulation; human gastric cancer stem cells; shrimp; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methylated lncRNAs suppress apoptosis of gastric cancer stem cells via the lncRNA-miRNA/protein axis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Apr 10;29(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00568-8. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38600465 Free PMC article.
-
miR-98-5p inhibits gastric cancer cell stemness and chemoresistance by targeting branched-chain aminotransferases 1.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 1;276:119405. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119405. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Life Sci. 2021. Retraction in: Life Sci. 2024 Sep 1;352:122888. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122888. PMID: 33798550 Retracted.
-
Shrimp miRNA suppresses the stemness of human cancer stem cells via the PIN1 pathway.FASEB J. 2019 Oct;33(10):10767-10779. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900395RR. Epub 2019 Jul 5. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31284761
-
An Updated Review of the Contribution of Noncoding RNAs to the Progression of Gastric Cancer Stem Cells: Molecular Mechanisms of Viability, Invasion, and Chemoresistance of Gastric Cancer Stem Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;17(5):440-445. doi: 10.2174/1574888X17666220126143302. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35081895 Review.
-
Dysregulated expression and functions of microRNA-330 in cancers: A potential therapeutic target.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Feb;146:112600. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112600. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34968919
References
-
- Galván-Alvarez D., Mendoza-Cano F., Hernández-López J., Sánchez-Paz A. Experimental evidence of metabolic disturbance in the white shrimp Penaeus vannamei induced by the Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012;111:60–67. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2012.06.005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

