The Diversity and Community Composition of Three Plants' Rhizosphere Fungi in Kaolin Mining Areas
- PMID: 38786661
- PMCID: PMC11121986
- DOI: 10.3390/jof10050306
The Diversity and Community Composition of Three Plants' Rhizosphere Fungi in Kaolin Mining Areas
Abstract
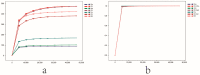
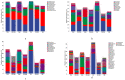
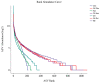
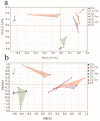
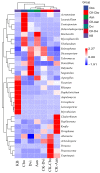
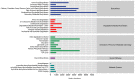
Mining activities in the kaolin mining area have led to the disruption of the ecological health of the mining area and nearby soils, but the effects on the fungal communities in the rhizosphere soils of the plants are not clear. Three common plants (Conyza bonariensis, Artemisia annua, and Dodonaea viscosa) in kaolin mining areas were selected and analyzed their rhizosphere soil fungal communities using ITS sequencing. The alpha diversity indices (Chao1, Shannon, Simpson, observed-species, pielou-e) of the fungal communities decreased to different extents in different plants compared to the non-kauri mining area. The β-diversity (PCoA, NMDS) analysis showed that the rhizosphere soil fungal communities of the three plants in the kaolin mine area were significantly differentiated from those of the control plants grown in the non-kaolin mine area, and the extent of this differentiation varied among the plants. The analysis of fungal community composition showed that the dominant fungi in the rhizosphere fungi of C. bonariensis and A. annua changed, with an increase in the proportion of Mycosphaerella (genus) by about 20% in C. bonariensis and A. annua. An increase in the proportion of Didymella (genus) by 40% in D. viscosa was observed. At the same time, three plant rhizosphere soils were affected by kaolin mining activities with the appearance of new fungal genera Ochrocladosporium and Plenodomus. Predictive functional potential analysis of the samples revealed that a significant decrease in the potential of functions such as biosynthesis and glycolysis occurred in the rhizosphere fungal communities of kaolin-mined plants compared to non-kaolin-mined areas. The results show that heavy metals and plant species are the key factors influencing these changes, which suggests that selecting plants that can bring more abundant fungi can adapt to heavy metal contamination to restore soil ecology in the kaolin mining area.
Keywords: functional potential; fungal diversity; kaolinite; mining activities; rhizosphere fungi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The impact of kaolin mining activities on bacterial diversity and community structure in the rhizosphere soil of three local plants.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1424687. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1424687. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39314884 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly Mechanisms and Functional Adaptations of Soil Fungal Communities of Different Plant Rhizospheres in Ilmenite Mining Area.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;11(3):165. doi: 10.3390/jof11030165. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137204 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly Mechanism of Rhizosphere Fungi in Plant Restoration in Lead Zinc Mining Areas.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 30;15(11):1398. doi: 10.3390/genes15111398. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39596598 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of rhizosphere bacterial diversity and composition in a metal hyperaccumulator (Boehmeria nivea) and a nonaccumulator (Artemisia annua) in an antimony mine.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 May;132(5):3432-3443. doi: 10.1111/jam.15486. Epub 2022 Feb 26. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35156279
-
Microbes from mined sites: Harnessing their potential for reclamation of derelict mine sites.Environ Pollut. 2017 Nov;230:495-505. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.056. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Environ Pollut. 2017. PMID: 28688926 Review.
Cited by
-
The Easily Overlooked Effect of Global Warming: Diffusion of Heavy Metals.Toxics. 2024 May 30;12(6):400. doi: 10.3390/toxics12060400. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 38922080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity and Functional Insights into Endophytic Fungi in Halophytes from West Ordos Desert Ecosystems.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Jan 4;11(1):30. doi: 10.3390/jof11010030. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852449 Free PMC article.
-
Three local plants adapt to ecological restoration of abandoned lead-zinc mines through assembly of rhizosphere bacterial communities.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 10;16:1533965. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1533965. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39996083 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of kaolin mining activities on bacterial diversity and community structure in the rhizosphere soil of three local plants.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1424687. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1424687. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39314884 Free PMC article.
-
Cyperus esculentus var. sativus Adapts to Multiple Heavy Metal Stresses Through the Assembly of Endophytic Microbial Communities.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jan 16;14(1):83. doi: 10.3390/biology14010083. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jacquet A., Geatches D.L., Clark S.J., Greenwell H.C. Understanding cationic polymer adsorption on mineral surfaces: Kaolinite in cement aggregates. Minerals. 2018;8:130. doi: 10.3390/min8040130. - DOI
-
- Awwad A., Amer M., Al-aqarbeh M. TiO2-kaolinite nanocomposite prepared from the Jordanian Kaolin clay: Adsorption and thermodynamics of Pb (II) and Cd (II) ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Int. 2020;6:168–178.
-
- Banu H.A.T., Karthikeyan P., Vigneshwaran S., Meenakshi S. Adsorptive performance of lanthanum encapsulated biopolymer chitosan-kaolin clay hybrid composite for the recovery of nitrate and phosphate from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020;154:188–197. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.074. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

