Unraveling the Role of Cuticular Protein 3-like (HvCP3L) in the Chitin Pathway through RNAi and Methoxyfenozide Stress Response in Heortia vitessoides Moore
- PMID: 38786918
- PMCID: PMC11122451
- DOI: 10.3390/insects15050362
Unraveling the Role of Cuticular Protein 3-like (HvCP3L) in the Chitin Pathway through RNAi and Methoxyfenozide Stress Response in Heortia vitessoides Moore
Abstract
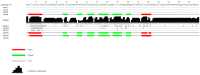
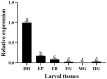
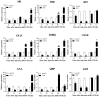
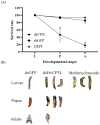
Cuticle proteins (CPs) constitute a multifunctional family; however, the physiological role of Cuticle Protein 3-like (CP3L) in Heortia vitessoides Moore remains largely unclear. In this study, we cloned the HvCP3L gene from the transcriptional library of Heortia vitessoides Moore. RT-qPCR results revealed that HvCP3L exhibited high expression levels during the larval stage of Heortia vitessoides Moore, particularly at the L5D1 stage, observed in both larval and adult heads. Through RNA interference, we successfully silenced the HvCP3L gene, resulting in a significant reduction in the survival rate of Heortia vitessoides Moore, with the survival rate from larvae to adults plummeting to a mere 17.7%, accompanied by phenotypic abnormalities. Additionally, we observed that the knockdown of HvCP3L led to the inhibition of genes in the chitin pathway. Following exposure to methoxyfenozide stress, the HvCP3L gene exhibited significant overexpression, coinciding with phenotypic abnormalities. These findings underscore the pivotal role of HvCP3L in the growth and development of Heortia vitessoides Moore.
Keywords: Heortia vitessoides Moore; RNA interference; chitin pathway; cuticular proteins; growth and development; methoxyfenozide stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

