An Algoclay-Based Decontaminant Decreases Exposure to Aflatoxin B1, Ochratoxin A, and Deoxynivalenol in a Toxicokinetic Model, as well as Supports Intestinal Morphology, and Decreases Liver Oxidative Stress in Broiler Chickens Fed a Diet Naturally Contaminated with Deoxynivalenol
- PMID: 38787059
- PMCID: PMC11125753
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16050207
An Algoclay-Based Decontaminant Decreases Exposure to Aflatoxin B1, Ochratoxin A, and Deoxynivalenol in a Toxicokinetic Model, as well as Supports Intestinal Morphology, and Decreases Liver Oxidative Stress in Broiler Chickens Fed a Diet Naturally Contaminated with Deoxynivalenol
Abstract
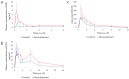
The aims of this study were (i) to determine the effect of an algoclay-based decontaminant on the oral availability of three mycotoxins (deoxynivalenol; DON, ochratoxin A; OTA, and aflatoxin B1; AFB1) using an oral bolus model and (ii) to determine the effect of this decontaminant on the performance, intestinal morphology, liver oxidative stress, and metabolism, in broiler chickens fed a diet naturally contaminated with DON. In experiment 1, sixteen 27-day-old male chickens (approximately 1.6 kg body weight; BW) were fasted for 12 h and then given a bolus containing either the mycotoxins (0.5 mg DON/kg BW, 0.25 mg OTA/kg BW, and 2.0 mg AFB1/kg BW) alone (n = 8) or combined with the decontaminant (2.5 g decontaminant/kg feed; circa 240 mg/kg BW) (n = 8). Blood samples were taken between 0 h (before bolus administration) and 24 h post-administration for DON-3-sulphate, OTA, and AFB1 quantification in plasma. The algoclay decontaminant decreased the relative oral bioavailability of DON (39.9%), OTA (44.3%), and AFB1 (64.1%). In experiment 2, one-day-old male Ross broilers (n = 600) were divided into three treatments with ten replicates. Each replicate was a pen with 20 birds. The broiler chickens were fed a control diet with negligible levels of DON (0.19-0.25 mg/kg) or diets naturally contaminated with moderate levels of DON (2.60-2.91 mg/kg), either supplemented or not with an algoclay-based decontaminant (2 g/kg diet). Jejunum villus damage was observed on day 28, followed by villus shortening on d37 in broiler chickens fed the DON-contaminated diet. This negative effect was not observed when the DON-contaminated diet was supplemented with the algoclay-based decontaminant. On d37, the mRNA expression of glutathione synthetase was significantly increased in the liver of broiler chickens fed the DON-contaminated diet. However, its expression was similar to the control when the birds were fed the DON-contaminated diet supplemented with the algoclay-based decontaminant. In conclusion, the algoclay-based decontaminant reduced the systemic exposure of broiler chickens to DON, OTA, and AFB1 in a single oral bolus model. This can be attributed to the binding of the mycotoxins in the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, dietary contamination with DON at levels between 2.69 and 2.91 mg/kg did not impair production performance but had a negative impact on broiler chicken intestinal morphology and the liver redox system. When the algoclay-based decontaminant was added to the diet, the harm caused by DON was no longer observed. This correlates with the results obtained in the toxicokinetic assay and can be attributed to a decreased absorption of DON.
Keywords: Fusarium; algae; broiler chickens; intestine; liver; mycotoxins; production performance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. M.G. and M.A.R. are employees of Olmix SA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ameliorative effect of a microbial feed additive on infectious bronchitis virus antibody titer and stress index in broiler chicks fed deoxynivalenol.Poult Sci. 2012 Apr;91(4):800-7. doi: 10.3382/ps.2011-01741. Poult Sci. 2012. PMID: 22399717 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of a Yeast β-Glucan on the Performance, Intestinal Integrity, and Liver Function of Broiler Chickens Fed a Diet Naturally Contaminated with Fusarium Mycotoxins.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jan 23;17(2):51. doi: 10.3390/toxins17020051. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39998068 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of addition of a probiotic microorganism to broiler diets contaminated with deoxynivalenol on performance and histological alterations of intestinal villi of broiler chickens.Poult Sci. 2006 Jun;85(6):974-9. doi: 10.1093/ps/85.6.974. Poult Sci. 2006. PMID: 16776464
-
Individual and combined occurrences of the prevalent mycotoxins in commercial feline and canine food.Mycotoxin Res. 2024 Nov;40(4):547-558. doi: 10.1007/s12550-024-00545-2. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Mycotoxin Res. 2024. PMID: 38990416 Review.
-
Aflatoxin B1: Challenges and Strategies for the Intestinal Microbiota and Intestinal Health of Monogastric Animals.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jan 17;17(1):43. doi: 10.3390/toxins17010043. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The PGC-1α/SIRT3 pathway mediates the effect of DON on mitochondrial autophagy and liver injury in mice.Mycotoxin Res. 2025 Aug;41(3):499-511. doi: 10.1007/s12550-025-00601-5. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Mycotoxin Res. 2025. PMID: 40668539
References
-
- Osselaere A., Santos R., Hautekiet V., De Backer P., Chiers K., Ducatelle R., Croubels S. Deoxynivalenol impairs hepatic and intestinal gene expression of selected oxidative stress, tight junction and inflammation proteins in broiler chickens, but addition of an adsorbing agent shifts the effects to the distal parts of the small intestine. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e69014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EC-European Commission Commission Recommendation 2016/1319/EC of 29 July 2016 Amending Commission Recommendation 2006/576/EC on the presence of deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, ochratoxin A, T-2 and HT-2 and fumonisins in products intended for animal feeding. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2016;L208:58–60.
-
- EFSA CONTAM Panel (EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain) Schrenk D., Bignami M., Bodin L., Chipman J.K., del Mazo J., Grasl-Kraupp B., Hogstrand C., Leblanc J.-C., Nielsen E., et al. Scientific Opinion on the assessment of information as regards the toxicity of deoxynivalenol for horses and poultry. EFSA J. 2023;21:e07806. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

