Approaches for the Efficient Removal of Fluoride from Groundwater: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 38787085
- PMCID: PMC11126082
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics12050306
Approaches for the Efficient Removal of Fluoride from Groundwater: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
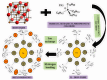
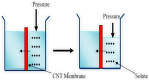
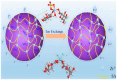
Contamination of groundwater with fluoride represents a significant global issue, with high concentrations posing serious public health threats. While fluoride is a critical element in water, excessive levels can be detrimental to human health and potentially life-threatening. Addressing the challenge of removing fluoride from underground water sources via nanotechnological approaches is a pressing concern in environmental science. To collate relevant information, extensive literature searches were conducted across multiple databases, including Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, the American Chemical Society, Elsevier, Springer, and the Royal Society of Chemistry. VOS Viewer software version 1.6.20 was employed for a systematic review. This article delivers an exhaustive evaluation of various groundwater fluoride removal techniques, such as adsorption, membrane filtration, electrocoagulation, photocatalysis, and ion exchange. Among these, the application of nanoparticles emerges as a notable method. The article delves into nano-compounds, optimizing conditions for the fluoride removal process and benchmarking their efficacy against other techniques. Studies demonstrate that advanced nanotechnologies-owing to their rapid reaction times and potent oxidation capabilities-can remove fluoride effectively. The implementation of nanotechnologies in fluoride removal not only enhances water quality but also contributes to the safeguarding of human health.
Keywords: VOS Viewer; advanced oxidation process; groundwater remediation; human health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Chamanehpour E., Sayadi M.H., Yousefi E. The Potential Evaluation of Groundwater Pollution Based on the Intrinsic and the Specific Vulnerability Index. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020;10:100313. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100313. - DOI
-
- Alhendal M., Nasir M.J., Hashim K.S., Amoako-Attah J., Al-Faluji D., Muradov M., Kot P., Abdulhadi B. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. Volume 888 IOP Publishing; Bristol, UK: 2020. Cost-Effective Hybrid Filter for Remediation of Water from Fluoride.
-
- Derakhshani R., Raoof A., Mahvi A.H., Chatrouz H. Similarities in the Fingerprints of Coal Mining Activities, High Ground Water Fluoride, and Dental Fluorosis in Zarand District, Kerman Province, Iran. Fluoride. 2020;53:257–267.
-
- Derakhshani R., Tavallaie M., Raoof M., Mohammadi T.M., Abbasnejad A., Haghdoostf A.A. Occurrence of Fluoride in Groundwater of Zarand Region, Kerman Province, Iran. Fluoride. 2014;47:133–138.
-
- Ndé-Tchoupé A.I., Crane R.A., Mwakabona H.T., Noubactep C., Njau K.N. Technologies for Decentralized Fluoride Removal: Testing Metallic Iron-Based Filters. Water. 2015;7:6657. doi: 10.3390/w7126657. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

