Integrating Epigenetics, Proteomics, and Metabolomics to Reveal the Involvement of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Oridonin-Induced Reproductive Toxicity
- PMID: 38787118
- PMCID: PMC11126149
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics12050339
Integrating Epigenetics, Proteomics, and Metabolomics to Reveal the Involvement of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Oridonin-Induced Reproductive Toxicity
Abstract
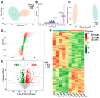
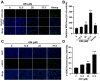
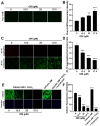
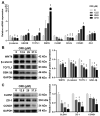
Oridonin is the primary active component in the traditional Chinese medicine Rabdosia rubescens, displaying anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and antibacterial effects. It is widely employed in clinical therapy for acute and chronic pharyngitis, tonsillitis, as well as bronchitis. Nevertheless, the clinical application of oridonin is significantly restricted due to its reproductive toxicity, with the exact mechanism remaining unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanism of oridonin-induced damage to HTR-8/SVneo cells. Through the integration of epigenetics, proteomics, and metabolomics methodologies, the mechanisms of oridonin-induced reproductive toxicity were discovered and confirmed through fluorescence imaging, RT-qPCR, and Western blotting. Experimental findings indicated that oridonin altered m6A levels, gene and protein expression levels, along with metabolite levels within the cells. Additionally, oridonin triggered oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage, leading to a notable decrease in WNT6, β-catenin, CLDN1, CCND1, and ZO-1 protein levels. This implied that the inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and disruption of tight junction might be attributed to the cytotoxicity induced by oridonin and mitochondrial dysfunction, ultimately resulting in damage to HTR-8/SVneo cells.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway; mitochondrial dysfunction; oridonin; reproductive toxicity; tight junction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multiomics profiling uncovers curdione-induced reproductive toxicity in HTR-8/SVneo cells.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 27;10(21):e38650. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38650. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524727 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in induction of apoptosis by oridonin in colon cancer COLO205 cells.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Sep;8(5):1782-1794. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.08.25. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116929 Free PMC article.
-
Oridonin inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of human neurocytoma cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):3333-3340. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8977. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127932 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of oridonin against osteoporosis by regulating immunity and activating the Wnt3a/β-catenin/VEGF pathway in ovariectomized mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 May;118:110011. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110011. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36924567 Review.
-
Oridonin: A Review of Its Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 5;12:645824. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.645824. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34295243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combining Multiple Omics with Molecular Dynamics Reveals SCP2-Mediated Cytotoxicity Effects of Aflatoxin B1 in SW480 Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Aug 24;16(9):375. doi: 10.3390/toxins16090375. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330833 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Profiling of Transcriptome and m6A Epitranscriptome Uncovers the Neurotoxic Effects of Yunaconitine on HT22 Cells.Evol Bioinform Online. 2024 Oct 12;20:11769343241290461. doi: 10.1177/11769343241290461. eCollection 2024. Evol Bioinform Online. 2024. PMID: 39483791 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing cancer therapy: advanced nanovehicle delivery systems for oridonin.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 3;15:1476739. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1476739. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39691396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Y., Wang L., Zi Y., Zhang L., Guo Y., Huang Y. Oridonin effectively reverses the drug resistance of cisplatin involving induction of cell apoptosis and inhibition of MMP expression in human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017;24:678–686. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.01.042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2021J01409/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
- 2021J05045/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
- 2021CXA033/Science and Technology Plan Project of Fujian Provincial Health Commission
- 2020Y9155/Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Joint Fund Project
- 82104520/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

