Molecular Identification and Survey of Trichomonad Species in Pigs in Shanxi Province, North China
- PMID: 38787175
- PMCID: PMC11125679
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci11050203
Molecular Identification and Survey of Trichomonad Species in Pigs in Shanxi Province, North China
Abstract
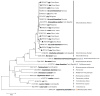
Several trichomonad species have already been identified in pigs, and their pathogenic potential may not be ruled out. To date, however, no information is available regarding the prevalence of trichomonads in pigs in Shanxi Province, North China. In the present study, a total of 362 fecal samples collected from pigs in three representative counties (Qi, Jishan, and Shanyin) in this province were examined for Tetratrichomonas buttreyi, Tritrichomonas foetus, and Pentatrichomonas hominis using a nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with primers targeting the small subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU rRNA) gene. The overall prevalence of T. buttreyi was 49.72%, and region and age were found to be significantly associated with T. buttreyi infection, respectively. Only one pig fecal sample from Qi County was found to be positive for T. foetus, and all samples were negative for P. hominis. Molecular evolutionary analysis revealed that some T. buttreyi isolates showed complete genetic identity with those reported previously, and some T. buttreyi isolates and one T. foetus isolate showed minor allelic variations compared with those reported previously. This is the report of the molecular epidemiology of T. foetus and T. buttreyi in pigs in Shanxi Province, North China. These findings not only enrich the knowledge on the distribution of these trichomonad species in pigs in China but also provide baseline information for planning future research and control strategies.
Keywords: Shanxi Province; pigs; prevalence; sequence analysis; trichomonads.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular Identification and Survey of Tetratrichomonas buttreyi and Pentatrichomonas hominis in Cattle in Shanxi Province, North China.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;15(13):1899. doi: 10.3390/ani15131899. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40646798 Free PMC article.
-
First Molecular Detection and Genetic Characterization of Tetratrichomonas buttreyi and Pentatrichomonas hominis in Donkeys in Shanxi Province, China.Animals (Basel). 2024 Sep 12;14(18):2651. doi: 10.3390/ani14182651. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335241 Free PMC article.
-
The First Report of Tritrichomonas Foetus and Tetratrichomonas Buttreyi in Raccoon Dogs (Nyctereutes Procyonoides) in China.Acta Parasitol. 2024 Sep;69(3):1352-1358. doi: 10.1007/s11686-024-00858-3. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Acta Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38888726
-
Survey and Molecular Characterization of Trichomonads in Pigs in Anhui Province, East China, 2014.Iran J Parasitol. 2018 Oct-Dec;13(4):602-610. Iran J Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 30697314 Free PMC article.
-
What is known about Tritrichomonas foetus infection in cats?Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2019 Jan-Mar;28(1):1-11. doi: 10.1590/S1984-29612019005. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2019. PMID: 30892464 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Identification and Survey of Tetratrichomonas buttreyi and Pentatrichomonas hominis in Cattle in Shanxi Province, North China.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;15(13):1899. doi: 10.3390/ani15131899. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40646798 Free PMC article.
-
Existence of Pentatrichomonas hominis in Tibetan Antelope (Pantholops hodgsonii).Front Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 5;12:1493928. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1493928. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 39974160 Free PMC article.
-
First Molecular Detection and Genetic Characterization of Tetratrichomonas buttreyi and Pentatrichomonas hominis in Donkeys in Shanxi Province, China.Animals (Basel). 2024 Sep 12;14(18):2651. doi: 10.3390/ani14182651. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335241 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Pentatrichomonas hominis infection in wild rodents.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Mar 28;21(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04604-3. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40155971 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of trichomonads in induced sputum from asthma patients in Korea.Parasites Hosts Dis. 2025 Aug;63(3):254-257. doi: 10.3347/PHD.25028. Epub 2025 Aug 20. Parasites Hosts Dis. 2025. PMID: 40888019 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- SXBYKY2021019/Shanxi Province Excellent Doctoral Work Award-Scientific Research Project
- RFSXIHLT202101/Research Fund of Shanxi Province for Introduced High-level Leading Talents
- 20211331-13/Fund for Shanxi "1331 Project"
- 2021XG001/Special Research Fund of Shanxi Agricultural University for High-level Talents
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

