miR-329b-5p Affects Sheep Intestinal Epithelial Cells against Escherichia coli F17 Infection
- PMID: 38787178
- PMCID: PMC11126089
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci11050206
miR-329b-5p Affects Sheep Intestinal Epithelial Cells against Escherichia coli F17 Infection
Abstract
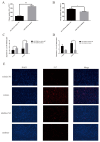
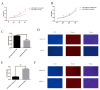
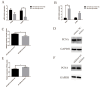
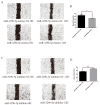
Diarrhea is the most common issue in sheep farms, typically due to pathogenic Escherichia coli (E. coli) infections, such as E. coli F17. microRNA, a primary type of non-coding RNA, has been shown to be involved in diarrhea caused by pathogenic E. coli. To elucidate the profound mechanisms of miRNA in E. coli F17 infections, methods such as E. coli F17 adhesion assay, colony counting assay, relative quantification of bacterial E. coli fimbriae gene expression, indirect immune fluorescence (IF), Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU), Western blotting (WB), and scratch assay were conducted to investigate the effect of miR-329b-5p overexpression/knock-down on E. coli F17 susceptibility of sheep intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). The findings indicated that miR-329b-5p enhances the E. coli F17 resistance of sheep IECs to E.coli F17 by promoting adhesion between E. coli F17 and IEC, as well as IEC proliferation and migration. In summary, miR-329b-5p plays a crucial role in the defense of sheep IECs against E. coli F17 infection, providing valuable insights into its mechanism of action.
Keywords: Escherichia coli F17; intestinal epithelial cells; micro RNA; sheep diarrhea.
Conflict of interest statement
Yeqing Wang and Rui Su are employed in Suzhou Stud Farm Co., Ltd. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression analysis of TLR signaling pathway genes under lipopolysaccharide-induced and E. coli F17-infected sheep intestinal epithelial cells.Anim Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;34(5):1815-1821. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2022.2052305. Epub 2022 May 11. Anim Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35544537
-
Sheep β-Defensin 2 Regulates Escherichia coli F17 Resistance via NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Ovine Intestinal Epithelial Cells.Biology (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;10(12):1356. doi: 10.3390/biology10121356. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943272 Free PMC article.
-
AFA and F17 adhesins produced by pathogenic Escherichia coli strains in domestic animals.Vet Res. 1999 Mar-Jun;30(2-3):317-42. Vet Res. 1999. PMID: 10367361 Review.
-
Non-Coding Transcriptome Provides Novel Insights into the Escherichia coli F17 Susceptibility of Sheep Lamb.Biology (Basel). 2022 Feb 22;11(3):348. doi: 10.3390/biology11030348. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336723 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and specific detection of F17-related pilin and adhesin genes in diarrheic and septicemic Escherichia coli strains by multiplex PCR.J Clin Microbiol. 1996 Dec;34(12):2921-8. doi: 10.1128/jcm.34.12.2921-2928.1996. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8940423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kolenda R., Burdukiewicz M., Schierack P. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of pathogenic Escherichia coli of calves and the role of calves as reservoirs for human pathogenic E. coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015;5:23. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 32061143036/National Natural Science Foundation of China-CGIAR
- 32172689/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22KJA230001, 22KJD230003/the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
- PZCZ201739/Major New Varieties of Agricultural Projects in Jiangsu Province
- CX(23)1036/Jiangsu Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Fund
- BZ2023009/the Project of Jiangsu Innovation Support Programme for International Science and Technology Cooperation - "Belt and Road" Innovation Cooperation
- YZ2023222/Yangzhou Meat Sheep Industry Public Service Platform
- JILAR-KF202205/the Distinguished Talents Project Foundation of Yangzhou University, and the Open Project Pro-gram of Joint International Research Laboratory of Agriculture and Agri-Product Safety, the Min-istry Education of China, Yangzhou University
- G2022014148L/the High-end Foreign Expert Introduction Project
- (2022)2-323/the Jiangsu 333 Distinguished Talents Project Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

