Therapeutic Applications of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin
- PMID: 38787206
- PMCID: PMC11123898
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13050354
Therapeutic Applications of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin
Abstract
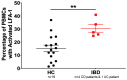
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is a Gram-negative oral bacterium that has been primarily studied for its role in causing periodontal disease. The bacterium has also been implicated in several systemic diseases such as endocarditis and soft tissue abscesses. Leukotoxin (LtxA) is perhaps the best studied protein virulence factor from A. actinomycetemcomitans. The protein can rapidly destroy white blood cells (WBCs), helping the bacterium to subvert the host immune system. The functional receptor for LtxA is lymphocyte function associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), which is expressed exclusively on the surfaces of WBCs. Bacterial expression and secretion of the protein are highly regulated and controlled by a number of genetic and environmental factors. The mechanism of LtxA action on WBCs varies depending on the type of cell that is being killed, and the protein has been shown to activate numerous cell death pathways in susceptible cells. In addition to serving as an important virulence factor for the bacterium, because of its exquisite specificity and rapid activity, LtxA is also being investigated as a therapeutic agent that may be used to treat diseases such as hematological malignancies and autoimmune/inflammatory diseases. It is our hope that this review will inspire an increased intensity of research related to LtxA and its effect on Aggressive Periodontitis, the disease that led to its initial discovery.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; LFA-1; allergic asthma; autoimmune disease; drug development; inflammation; inflammatory bowel disease; leukemia; lymphoma; protein drug; translational research; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
SCK owns stock in the company that has licensed the use of LtxA for therapeutic applications (Actinobac). The funders had no role in the design of the study; the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; the writing of the manuscript; or the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Haubek D., Ennibi O.K., Poulsen K., Vaeth M., Poulsen S., Kilian M. Risk of aggressive periodontitis in adolescent carriers of the JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans in Morocco: A prospective longitudinal cohort study. Lancet. 2008;371:237–242. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60135-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

