Calmodulin-like 5 promotes PEDV replication by regulating late-endosome synthesis and innate immune response
- PMID: 38789039
- PMCID: PMC11280258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virs.2024.05.006
Calmodulin-like 5 promotes PEDV replication by regulating late-endosome synthesis and innate immune response
Abstract
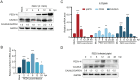
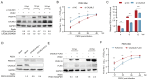
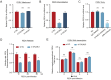
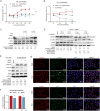
The infection caused by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) is associated with high mortality in piglets worldwide. Host factors involved in the efficient replication of PEDV, however, remain largely unknown. Our recent proteomic study in the virus-host interaction network revealed a significant increase in the accumulation of CALML5 (EF-hand protein calmodulin-like 5) following PEDV infection. A further study unveiled a biphasic increase of CALML5 in 2 and 12 h after viral infection. Similar trends were observed in the intestines of piglets in the early and late stages of the PEDV challenge. Moreover, CALML5 depletion reduced PEDV mRNA and protein levels, leading to a one-order-of-magnitude decrease in virus titer. At the early stage of PEDV infection, CALML5 affected the endosomal trafficking pathway by regulating the expression of endosomal sorting complex related cellular proteins. CALML5 depletion also suppressed IFN-β and IL-6 production in the PEDV-infected cells, thereby indicating its involvement in negatively regulating the innate immune response. Our study reveals the biological function of CALML5 in the virology field and offers new insights into the PEDV-host cell interaction.
Keywords: EF-hand protein calmodulin-like 5 (CALML5); Innate immune response; Late endosomes; Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV).
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Innate Immune Evasion of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus through Degradation of the FBXW7 Protein via the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0088921. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00889-21. Epub 2021 Sep 8. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34495699 Free PMC article.
-
Serum amyloid P component suppresses porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication through TLR4-mediated IFN-β signaling pathway.Vet Microbiol. 2025 May;304:110459. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2025.110459. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Vet Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40080977
-
Porcine Intestinal Enteroids: a New Model for Studying Enteric Coronavirus Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection and the Host Innate Response.J Virol. 2019 Feb 19;93(5):e01682-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01682-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30541861 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: A review of detection, inhibition of host gene expression and evasion of host innate immune.Microb Pathog. 2024 Oct;195:106873. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106873. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39173850 Review.
-
Host restriction factors against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: a mini-review.Vet Res. 2025 Mar 24;56(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01500-4. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40128890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barouch-Bentov R., Neveu G., Xiao F., Beer M., Bekerman E., Schor S., Campbell J., Boonyaratanakornkit J., Lindenbach B., Lu A., Jacob Y., Einav S. Hepatitis C virus proteins interact with the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) machinery via ubiquitination to facilitate viral envelopment. mBio. 2016;7 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deng L., Liang Y., Ariffianto A., Matsui C., Abe T., Muramatsu M., Wakita T., Maki M., Shibata H., Shoji I. Hepatitis C virus-induced ROS/JNK signaling pathway activates the E3 ubiquitin ligase itch to promote the release of HCV particles via polyubiquitylation of VPS4A. J. Virol. 2022;96 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

