Investigating the Transepithelial Transport and Enzymatic Stability of Lactononadecapeptide (NIPPLTQTPVVVPPFLQPE), a 19-Amino Acid Casein-Derived Peptide in Caco-2 Cells
- PMID: 38789103
- PMCID: PMC11157532
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c00974
Investigating the Transepithelial Transport and Enzymatic Stability of Lactononadecapeptide (NIPPLTQTPVVVPPFLQPE), a 19-Amino Acid Casein-Derived Peptide in Caco-2 Cells
Abstract
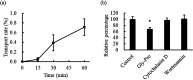
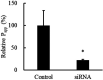
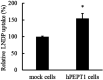
Lactononadecapeptide (LNDP; NIPPLTQTPVVVPPFLQPE), a casein-derived peptide comprising 19 residues, is known for its capacity to enhance cognitive function. This study aimed to explore the transepithelial transport and stability of LNDP. Results showed that LNDP retained over 90% stability after 2 h of treatment with gastrointestinal enzymes. The stability of LNDP on Caco-2 cell monolayers ranged from 93.4% ± 0.9% to 101.1% ± 1.2% over a period of 15-60 min, with no significant differences at each time point. The permeability of LNDP across an artificial lipid membrane was very low with the effective permeability of 3.6 × 10-11 cm/s. The Caco-2 assay demonstrated that LNDP could traverse the intestinal epithelium, with an apparent permeability of 1.22 × 10-6 cm/s. Its transport was significantly inhibited to 67.9% ± 5.0% of the control by Gly-Pro, a competitor of peptide transporter 1 (PEPT1). Furthermore, PEPT1 knockdown using siRNA significantly inhibited LNDP transport by 77.6% ± 1.9% in Caco-2 cell monolayers. The LNDP uptake in PEPT1-expressing HEK293 cells was significantly higher (54.5% ± 14.6%) than that in mock cells. These findings suggest that PEPT1 plays a crucial role in LNDP transport, and LNDP exhibits good resistance to gastrointestinal enzymes.
Keywords: Caco-2 cells; beta-casein; intestinal transport; lactononadecapeptide (LNDP); peptide; peptide transporter 1 (PEPT1).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): This research received funding from Asahi Group Holdings, Ltd., Japan. M.S., H.M., and T.H. are employed by Asahi Quality and Innovations Ltd., which is affiliated with Asahi Group Holdings Ltd. E.N., S.T., and T.O. state that the research was conducted without any financial interests that could be perceived as conflicts of interest. The funders did not influence the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, manuscript writing, or the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of PepT1 transport of food-derived antihypertensive peptides, Ile-Pro-Pro and Leu-Lys-Pro using in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo transport models.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017 Jun;115:276-284. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.03.007. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017. PMID: 28315445
-
Transport Versus Hydrolysis: Reassessing Intestinal Assimilation of Di- and Tripeptides by LC-MS/MS Analysis.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019 Nov;63(21):e1900263. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900263. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019. PMID: 31394017
-
Sodium caprate enables the blood pressure-lowering effect of Ile-Pro-Pro and Leu-Lys-Pro in spontaneously hypertensive rats by indirectly overcoming PepT1 inhibition.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018 Jul;128:179-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.04.021. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018. PMID: 29684535
-
Role of PEPT1in the transport of cinnabar in Caco-2 cells.Toxicol In Vitro. 2020 Mar;63:104747. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104747. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Toxicol In Vitro. 2020. PMID: 31838184
-
Regulation profile of the intestinal peptide transporter 1 (PepT1).Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Dec 8;11:3511-3517. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S151725. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 29263649 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Srivastava U.; Nataraj B. H.; Kumari M.; Kadyan S.; Puniya A. K.; Behare P. V.; Nagpal R. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory potency of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus NCDC24 fermented milk-derived peptides: A computationally guided in-vitro and ex-vivo investigation. Peptides 2022, 155, 17084310.1016/j.peptides.2022.170843. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

