HDAC activity is dispensable for repression of cell-cycle genes by DREAM and E2F:RB complexes
- PMID: 38789411
- PMCID: PMC11126580
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48724-0
HDAC activity is dispensable for repression of cell-cycle genes by DREAM and E2F:RB complexes
Abstract
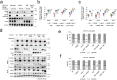
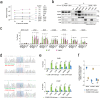
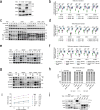
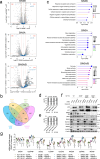
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) play a crucial role in transcriptional regulation and are implicated in various diseases, including cancer. They are involved in histone tail deacetylation and canonically linked to transcriptional repression. Previous studies suggested that HDAC recruitment to cell-cycle gene promoters via the retinoblastoma (RB) protein or the DREAM complex through SIN3B is essential for G1/S and G2/M gene repression during cell-cycle arrest and exit. Here we investigate the interplay among DREAM, RB, SIN3 proteins, and HDACs in the context of cell-cycle gene repression. Knockout of SIN3B does not globally derepress cell-cycle genes in non-proliferating HCT116 and C2C12 cells. Loss of SIN3A/B moderately upregulates several cell-cycle genes in HCT116 cells but does so independently of DREAM/RB. HDAC inhibition does not induce general upregulation of RB/DREAM target genes in arrested transformed or non-transformed cells. Our findings suggest that E2F:RB and DREAM complexes can repress cell-cycle genes without relying on HDAC activity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
HDAC activity is dispensable for repression of cell-cycle genes by DREAM and E2F:RB complexes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 28:2023.10.28.564489. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.28.564489. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 May 24;15(1):4450. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48724-0. PMID: 37961464 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

