Melatonin alleviates septic ARDS by inhibiting NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in alveolar macrophages
- PMID: 38789436
- PMCID: PMC11126704
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-024-01991-8
Melatonin alleviates septic ARDS by inhibiting NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in alveolar macrophages
Abstract
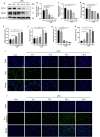
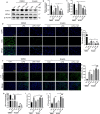
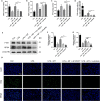
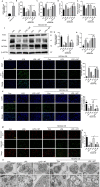
Ferroptosis is a novel form of programmed cell death which can exacerbate lung injury in septic acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Alveolar macrophages, crucial innate immune cells, play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of ARDS. Ferritinophagy is a process of ferritin degradation mediated by nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) which releases large amounts of iron ions thus promoting ferroptosis. Recent evidence revealed that inhibiting macrophage ferroptosis can effectively attenuate pulmonary inflammatory injury. Melatonin (MT), an endogenous neurohormone, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and can reduce septic ARDS. However, it is not clear whether MT's pulmonary protective effect is related to the inhibition of macrophage ferritinophagy. Our in vitro experiments demonstrated that MT decreased intracellular malondialdehyde (MDA), Fe2+, and lipid peroxidation levels, increased glutathione (GSH) levels and cell proliferation, and upregulated glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) and ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1) protein levels in LPS-treated macrophages. Mechanistically, the antiferroptotic effect of MT on LPS-treated macrophages was significantly compromised by the overexpression of NCOA4. Our in vivo experiments revealed that MT alleviated the protein expression of NCOA4 and FTH1 in the alveolar macrophages of septic mice. Furthermore, MT improved lipid peroxidation and mitigated damage in alveolar macrophages and lung tissue, ultimately increasing the survival rates of septic mice. These findings indicate that MT can inhibit ferroptosis in an NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy manner, thereby ameliorating septic ARDS.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
STAT3 signaling promotes cardiac injury by upregulating NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in high-fat-diet fed mice.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 May 20;201:111-125. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.003. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36940731
-
Ferritinophagy is involved in the zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced ferroptosis of vascular endothelial cells.Autophagy. 2021 Dec;17(12):4266-4285. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1911016. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33843441 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviated NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy protected RA FLSs from ferroptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation under hypoxia.Inflamm Res. 2024 Mar;73(3):363-379. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01842-9. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38189810
-
The Role of NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy in Ferroptosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1301:41-57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-62026-4_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34370287 Review.
-
The Role of NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy in Health and Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018 Oct 23;11(4):114. doi: 10.3390/ph11040114. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30360520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of machine learning and protein‑protein interaction network established one ATM‑DPP4‑TXN ferroptotic diagnostic model with experimental validation.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Sep;32(3):239. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13604. Epub 2025 Jul 4. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40613196 Free PMC article.
-
Ferritinophagy mediated by the AMPK/ULK1 pathway is involved in ferroptosis subsequent to ventilator-induced lung injury.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 24;25(1):440. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03076-7. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39719634 Free PMC article.
-
Aerosol inhalation of dimeric artesunate phospholipid-conjugated liposomes ameliorates inflammation, fibrosis, and ferroptosis in neonatal mice with hyperoxia-induced lung injury.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1542743. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1542743. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40761396 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Activates KEAP1/NRF2/PTGS2 Pathway to Attenuate Hyperoxia-Driven Ferroptosis in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jun 11;18:7571-7583. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S520404. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40524969 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on the role of calcium signaling in ferroptosis: a potential therapeutic strategy for sepsis-induced acute lung injury.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 17;11:1457882. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1457882. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39355841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

