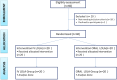
Intravenous versus oral 'L-ornithine-L-aspartate' in overt hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized comparative study
- PMID: 38789596
- PMCID: PMC11126676
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-62293-8
Intravenous versus oral 'L-ornithine-L-aspartate' in overt hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized comparative study
Abstract
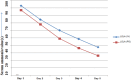
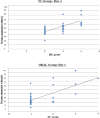
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE), a morbid ordeal affecting chronic liver disease patients always insists for the search of a rational, superior & infallible agent beyond the time-proven standards i.e., Lactulose & Rifaximin. In this RCT, we compared the efficacy of intravenous (IV) L-ornithine-L-aspartate(LOLA) versus Oral LOLA in patients with chronic liver disease(CLD) enduring overt Hepatic Encephalopathy(OHE). 40 CLD patients with OHE were randomly assigned IV or oral LOLA in a 1:1 ratio. Patients were graded for HE and monitored for serum ammonia levels from day 1 to day 5. The aim was to compare IV versus oral LOLA efficacy in HE grades improvement and its correlation with ammonia levels. The study was registered with clinical trials registry-India, CTRI/2020/12/029943. Baseline characteristics of patients in both groups were similar. The mean difference in ammonia levels from day 1 to day 5 was 55.4 ± 32.58 µmol/L in the IV LOLA group and 60.75 ± 13.82 µmol/L in the oral LOLA group (p = 0.511). Significant reductions in ammonia levels were observed from day 1 to day 5 within each group (p < 0.001). HE grade & ammonia correlated positively in both groups. LOLA, regardless of administration route, has demonstrated efficacy in OHE.
Keywords: l-ornithine-l-aspartate (LOLA); Child turcotte pugh (CTP); Overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE); Randomized controlled trial (RCT).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Butterworth RF, Kircheis G, Hilger N, McPhail MJW. Efficacy of l-ornithine l-aspartate for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy and hyperammonemia in cirrhosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018;8(3):301–313. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2018.05.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources