Spliceosomic dysregulation in pancreatic cancer uncovers splicing factors PRPF8 and RBMX as novel candidate actionable targets
- PMID: 38790138
- PMCID: PMC11459039
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13658
Spliceosomic dysregulation in pancreatic cancer uncovers splicing factors PRPF8 and RBMX as novel candidate actionable targets
Abstract
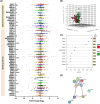
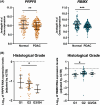
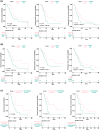
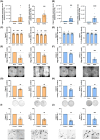
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly lethal cancer, characterized by late diagnosis and poor treatment response. Surgery is the only curative approach, only available to early-diagnosed patients. Current therapies have limited effects, cause severe toxicities, and minimally improve overall survival. Understanding of splicing machinery alterations in PDAC remains incomplete. Here, we comprehensively examined 59 splicing machinery components, uncovering dysregulation in pre-mRNA processing factor 8 (PRPF8) and RNA-binding motif protein X-linked (RBMX). Their downregulated expression was linked to poor prognosis and malignancy features, including tumor stage, invasion and metastasis, and associated with poorer survival and the mutation of key PDAC genes. Experimental modulation of these splicing factors in pancreatic cancer cell lines reverted their expression to non-tumor levels and resulted in decreased key tumor-related features. These results provide evidence that the splicing machinery is altered in PDAC, wherein PRPF8 and RBMX emerge as candidate actionable therapeutic targets.
Keywords: PRPF8; RBMX; pancreatic cancer; splicing; splicing factor.
© 2024 The Authors. Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bailey P, Chang DK, Nones K, Johns AL, Patch A‐M, Gingras M‐C, et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2016;531(7592):47–52. - PubMed
-
- Rogalska ME, Vivori C, Valcárcel J. Regulation of pre‐mRNA splicing: roles in physiology and disease, and therapeutic prospects. Nat Rev Genet. 2022;1–19:251–269. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- FERP2020/Fundación Eugenio Rodríguez Pascual
- BIO-0139/Junta de Andalucía
- UCO-202099901918904/Junta de Andalucía
- AEI/10.13039/501100011033/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PID2019-105201RB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PID2019-105564RB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- 203885/2017/Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Verona Vicenza Belluno e Ancona
- FIMPCUP_J38D19000690001/Fondazione Italiana per la Ricerca sulle Malattie del Pancreas
- BFU2016-80360-R/Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness
- FPU18/02275/Spanish Ministry of Universities
- FPU20/03958/Spanish Ministry of Universities
- Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red-Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición
- CA21116/European Cooperation in Science and Technology
- 26343/Fondazione AIRC per la Ricerca sul Cancro
- G2016/Grupo Español de Tumores Neuroendocrinos y Endocrinos
- G2019/Grupo Español de Tumores Neuroendocrinos y Endocrinos
- GJ2208/Grupo Español de Tumores Neuroendocrinos y Endocrinos
- CD19/00255/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- DTS20/00050/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- FI17/00282/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI17/02287/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI20/01301/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

