Cellular ROS and Antioxidants: Physiological and Pathological Role
- PMID: 38790707
- PMCID: PMC11117742
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13050602
Cellular ROS and Antioxidants: Physiological and Pathological Role
Abstract
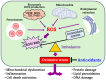
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive oxygen derivatives that include free radicals such as superoxide anion radical (O2•-) and hydroxyl radical (HO•), as well as non-radical molecules hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), peroxynitrite (ONOO-), and hypochlorous acid (HOCl) [...].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dikalova A., Clempus R., Lassegue B., Cheng G., McCoy J., Dikalov S., San Martin A., Lyle A., Weber D.S., Weiss D., et al. Nox1 overexpression potentiates angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular smooth muscle hypertrophy in transgenic mice. Circulation. 2005;112:2668–2676. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.538934. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

