Role of Epigenetic Modulation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Implications of Phytochemical Interventions
- PMID: 38790711
- PMCID: PMC11118909
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13050606
Role of Epigenetic Modulation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Implications of Phytochemical Interventions
Abstract
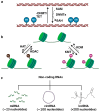
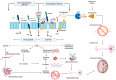
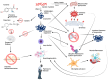
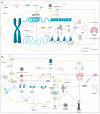
Epigenetics defines changes in cell function without involving alterations in DNA sequence. Neuroepigenetics bridges neuroscience and epigenetics by regulating gene expression in the nervous system and its impact on brain function. With the increase in research in recent years, it was observed that alterations in the gene expression did not always originate from changes in the genetic sequence, which has led to understanding the role of epigenetics in neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) including Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). Epigenetic alterations contribute to the aberrant expression of genes involved in neuroinflammation, protein aggregation, and neuronal death. Natural phytochemicals have shown promise as potential therapeutic agents against NDDs because of their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects in cellular and animal models. For instance, resveratrol (grapes), curcumin (turmeric), and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG; green tea) exhibit neuroprotective effects through their influence on DNA methylation patterns, histone acetylation, and non-coding RNA expression profiles. Phytochemicals also aid in slowing disease progression, preserving neuronal function, and enhancing cognitive and motor abilities. The present review focuses on various epigenetic modifications involved in the pathology of NDDs, including AD and PD, gene expression regulation related to epigenetic alterations, and the role of specific polyphenols in influencing epigenetic modifications in AD and PD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; epigenetic modulation; nutriepigenomics; phytochemicals; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurodegenerative diseases: Epigenetic regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Cell Signal. 2025 Jul;131:111715. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111715. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40089090 Review.
-
Epigenetic Modulation in Parkinson's Disease and Potential Treatment Therapies.Neurochem Res. 2021 Jul;46(7):1618-1626. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03334-w. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 33900517 Review.
-
The pivotal role of JAK/STAT and IRS/PI3K signaling pathways in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanistic approaches to polyphenols and alkaloids.Phytomedicine. 2023 Apr;112:154686. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154686. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36804755 Review.
-
Neurodegenerative diseases and catechins: (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate is a modulator of chronic neuroinflammation and oxidative stress.Front Nutr. 2024 Aug 1;11:1425839. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1425839. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39149548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Changes and Its Intervention in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Apr;42(3):577-595. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00979-z. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 33074454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the molecular mechanisms of curcumin in modulating memory impairment in neurodegenerative disorders.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 9;52(1):45. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10115-5. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39653966 Review.
-
Decoding Neurodegeneration: A Review of Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advances in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and ALS.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 24;25(23):12613. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312613. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain Neurotrophins and Plant Polyphenols: A Powerful Connection.Molecules. 2025 Jun 19;30(12):2657. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122657. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review on the impact of polyphenol supplementation and exercise on depression and brain function parameters.Behav Brain Funct. 2025 Mar 26;21(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12993-025-00273-2. Behav Brain Funct. 2025. PMID: 40140839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Redox Revolution in Brain Medicine: Targeting Oxidative Stress with AI, Multi-Omics and Mitochondrial Therapies for the Precision Eradication of Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 3;26(15):7498. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157498. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

