Sensory and Physical Properties of Fibrous Meat Analogs Made from Faba Bean, Pea, and Oat Using High-Moisture Extrusion
- PMID: 38790744
- PMCID: PMC11119597
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13101444
Sensory and Physical Properties of Fibrous Meat Analogs Made from Faba Bean, Pea, and Oat Using High-Moisture Extrusion
Abstract
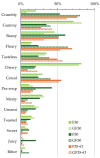
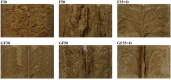
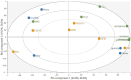
Faba bean is a promising source of ingredients for the production of meat analogs. However, sensory properties of faba bean, especially the bitter taste of the protein concentrate, restrict its use. Our aim was to assess the feasibility of two types of faba bean ingredients-flour (from germinated, gently heat-treated beans) and groat (from non-germinated, roasted beans)-in combination with pea protein isolate and oat fiber concentrate for producing meat analogs using high-moisture extrusion. We produced six samples using varying recipes, while maintaining constant process parameters. An untrained panel (55 participants) evaluated the samples for key sensory attributes (check-all-that-apply) and rated their pleasantness. The water absorption capacity and mechanical properties of the samples were assessed using instrumental measurements. The samples were frequently described as 'beany' and 'tasteless', but very rarely as 'bitter'. The most frequently cited attributes for mouthfeel varied between the samples containing 30% ('tough', 'gummy') and 50% ('crumbly', 'floury') of faba bean flour/groat and were associated with corresponding mechanical properties. On average, the sample containing a blend of faba bean groat and pea protein isolate (50% each) appeared to be the most pleasant. Our results suggest that faba bean groat with pea protein isolate enables the production of fibrous meat analogs with acceptable taste and texture, without the bitter off-taste.
Keywords: CATA; Vicia faba; consumers; hedonic value; meat alternative; plant-based protein; sensory evaluation; texture profile analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Wood P., Tavan M. A Review of the Alternative Protein Industry. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022;47:100869. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2022.100869. - DOI
-
- Lanz M., Hartmann C., Egan P., Siegrist M. Consumer Acceptance of Cultured, Plant-Based, 3D-Printed Meat and Fish Alternatives. Future Foods. 2024;9:100297. doi: 10.1016/j.fufo.2024.100297. - DOI
-
- Anusha Siddiqui S., Bahmid N.A., Mahmud C.M.M., Boukid F., Lamri M., Gagaoua M. Consumer Acceptability of Plant-, Seaweed-, and Insect-Based Foods as Alternatives to Meat: A Critical Compilation of a Decade of Research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023;63:6630–6651. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2036096. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

