Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Preservative Effects of Cinnamaldehyde and Clove Oil in Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fillets Stored at 4 °C
- PMID: 38790745
- PMCID: PMC11119078
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13101445
Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Preservative Effects of Cinnamaldehyde and Clove Oil in Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fillets Stored at 4 °C
Abstract
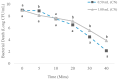
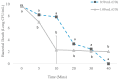
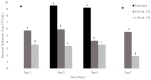
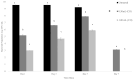
This study aimed to evaluate cinnamaldehyde (CN) and clove oil (CO) effectiveness in inhibiting growth and killing spoilage and total aerobic bacteria when overlaid with catfish fillet stored at 4 °C. A 1.00 mL concentration of CO inhibited growth by 2.90, 1.96, and 1.96 cm, respectively, for S. baltica, A. hydrophilia, and total bacteria. Similarly, treatment with 1.00 mL of CN resulted in ZIB of 2.17, 2.10, and 1.10 cm, respectively, for S. baltica, A. hydrophilia, and total bacteria from catfish exudates. Total bacteria from catfish exudates treated with 0.50 mL CN for 40 min, resulted in a 6.84 log decrease, and treatment with 1.00 mL resulted in a 5.66 log decrease at 40 min. Total bacteria exudates treated with 0.50 mL CO resulted in a 9.69 log reduction at 40 min. Total bacteria treated with 1.00 mL CO resulted in a 7.69 log decrease at 7 days, while untreated pads overlaid with catfish resulted in ≥9.00 CFU/mL. However, treated absorbent pads with catfish at 7 days, using 0.50 mL and 1.00 mL CN, had a bacterial recovery of 5.53 and 1.88 log CFU/mL, respectively. Furthermore, CO at 0.50 mL and 1.00 mL reduced the bacteria count to 5.21 and 1.53 log CFU/mL, respectively, at day 7.
Keywords: absorbent food pads; catfish; cinnamaldehyde; clove oil; essential oil; spoilage; storage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of virulent phages infecting Shewanella baltica and Shewanella putrefaciens, and their application for biopreservation of chilled channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus).Int J Food Microbiol. 2019 Mar 2;292:107-117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.12.020. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Int J Food Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30594742
-
Microbial quality and safety of X-ray irradiated fresh catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) fillets stored under CO2 atmosphere.J Food Sci. 2012 Sep;77(9):M533-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2012.02866.x. Epub 2012 Aug 17. J Food Sci. 2012. PMID: 22901245
-
The Microbiome of Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Treated with Natural Preservatives During Refrigerated Storage.Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 23;13(2):244. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020244. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005614 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of endogenous bacteria associated with catfish fillets using the Grovac process.J Food Prot. 2000 Sep;63(9):1231-9. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-63.9.1231. J Food Prot. 2000. PMID: 10983798
-
Reduction of Listeria monocytogenes on the surface of fresh channel catfish fillets by bacteriophage Listex P100.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010 Apr;7(4):427-34. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2009.0432. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010. PMID: 19958102
Cited by
-
Use of culinary ingredients as protective components during thermal heating of pumpkin oil.Food Chem X. 2025 Feb 13;26:102272. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102272. eCollection 2025 Feb. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40060959 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Effectiveness of Clove Oil in Decontamination of Ready-to-Eat Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.).Foods. 2025 Jan 14;14(2):249. doi: 10.3390/foods14020249. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39856915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mishra P., Sharma M., Kewat A. Spoilage in Fish and Shellfish Products. Limnology. 2022;2:59.
-
- Mishra S.P., Pradesh U. Significance of fish nutrients for human health. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2020;5:47–49.
-
- Venegas-Calerón M., Napier J.A. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2023. New alternative sources of omega-3 fish oil; pp. 343–398. - PubMed
-
- Krittanawong C., Isath A., Hahn J., Wang Z., Narasimhan B., Kaplin S.L., Jneid H., Virani S.S., Tang W.W. Fish consumption and cardiovascular health: A systematic review. Am. J. Med. 2021;134:713–720. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

