Based on CiteSpace Insights into Illicium verum Hook. f. Current Hotspots and Emerging Trends and China Resources Distribution
- PMID: 38790809
- PMCID: PMC11119909
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13101510
Based on CiteSpace Insights into Illicium verum Hook. f. Current Hotspots and Emerging Trends and China Resources Distribution
Abstract
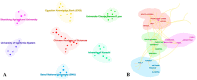
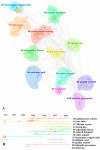
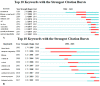
Illicium verum Hook. f. is a globally significant spice, which is recognized in China as a food-medicine homolog and extensively utilized across the pharmaceutical, food, and spice industries. China boasts the world's leading resources of I. verum, yet its comprehensive utilization remains relatively underexplored. Through a resource survey of I. verum and the application of bibliometric visualization using CiteSpace, this study analyzed 324 papers published in the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) from 1962 to 2023 and 353 core documents from China's three major databases (CNKI, Wanfang Database, and VIP Database). I. verum from Guangxi province towards various southern provinces in China, with autumn fruits exhibited superior quality and market value over their spring fruits. Literature in WOSCC emerged earlier, with a research emphasis on food science technology and pharmacology pharmacy domains. WOSCC research on I. verum could be divided into two phases: an embryonic period (1962-2001) and a growth period (2002-2023), showing an overall upward trend in publication. The three major Chinese databases contain a larger number of publications, with a focus on the food sector, which could be categorized into three stages: an embryonic period (1990-1999), a growth period (2000-2010), and a stable period (2011-2023), with an overall downward trend in publication. Both Chinese and international research hotspots converge on the medical applications of I. verum, with antioxidant bioactivity research emerging as a prevailing trend. This study delineated the resource distribution of I. verum across China and identified the research hotspots and trends both in China and internationally. The findings are beneficial for guiding researchers in swiftly establishing their research focus and furnishing decision-makers with a comprehensive reference for industry information.
Keywords: CiteSpace; Illicium verum; bibliometrics; resource.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
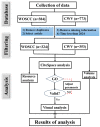
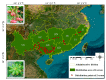
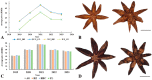
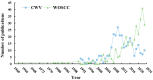

References
-
- Huang K.S., Li G.Q., An J.C., Li K.X. Developing situation of processing and utilization industry of characteristic resources of Star anise (Illicium verum) [(accessed on 25 March 2024)];Biomass Chem. Eng. 2020 54:6–12. Available online: https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCHG202006002.htm.
-
- Noumi E., Ahmad I., Adnan M., Patel H., Merghni A., Haddaji N., Bouali N., Alabbosh K.F., Kadri A., Caputo L., et al. Illicium verum L. (Star anise) essential oil: GC/MS profile, molecular docking study, in silico ADME profiling, quorum sensing, and biofilm-inhibiting effect on foodborne bacteria. Molecules. 2023;28:7691. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237691. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- George C.K. 24—Star anise. In: Peter K.V., editor. Handbook of Herbs and Spices. 2nd ed. Woodhead Publishing; Cambridge, UK: 2012. [(accessed on 25 March 2024)]. pp. 487–503. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780857090393/handbook-of-herbs-and-s....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

